SuperWarp: Supervised Learning and Warping on U-Net for Invariant Subvoxel-Precise Registration
Paper and Code
May 15, 2022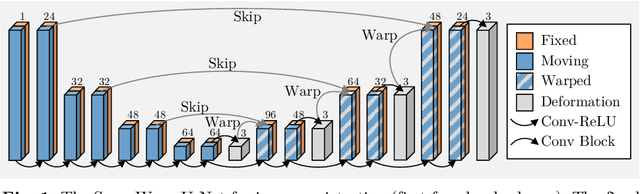

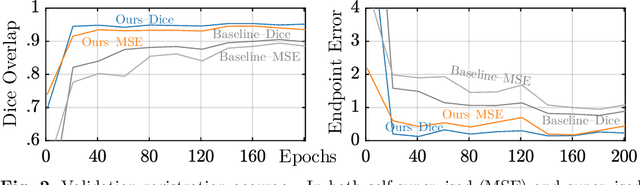
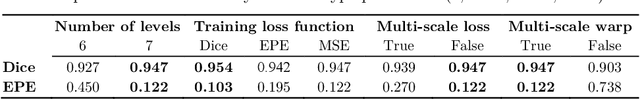
In recent years, learning-based image registration methods have gradually moved away from direct supervision with target warps to instead use self-supervision, with excellent results in several registration benchmarks. These approaches utilize a loss function that penalizes the intensity differences between the fixed and moving images, along with a suitable regularizer on the deformation. In this paper, we argue that the relative failure of supervised registration approaches can in part be blamed on the use of regular U-Nets, which are jointly tasked with feature extraction, feature matching, and estimation of deformation. We introduce one simple but crucial modification to the U-Net that disentangles feature extraction and matching from deformation prediction, allowing the U-Net to warp the features, across levels, as the deformation field is evolved. With this modification, direct supervision using target warps begins to outperform self-supervision approaches that require segmentations, presenting new directions for registration when images do not have segmentations. We hope that our findings in this preliminary workshop paper will re-ignite research interest in supervised image registration techniques. Our code is publicly available from https://github.com/balbasty/superwarp.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge