SoPhie: An Attentive GAN for Predicting Paths Compliant to Social and Physical Constraints
Paper and Code
Sep 20, 2018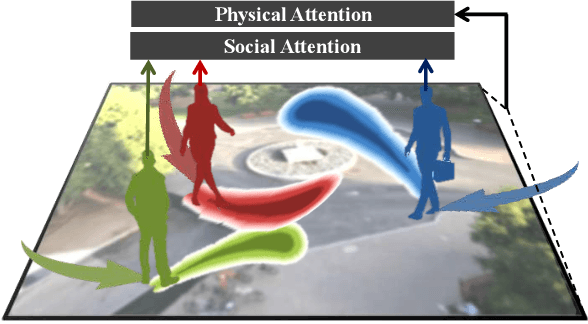
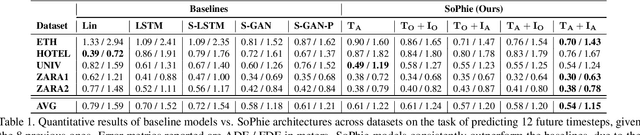
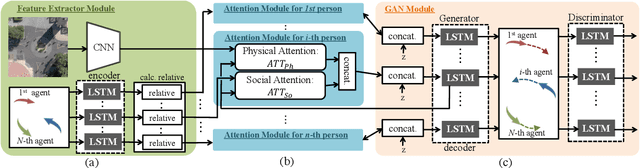
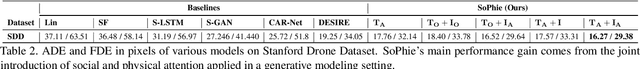
This paper addresses the problem of path prediction for multiple interacting agents in a scene, which is a crucial step for many autonomous platforms such as self-driving cars and social robots. We present \textit{SoPhie}; an interpretable framework based on Generative Adversarial Network (GAN), which leverages two sources of information, the path history of all the agents in a scene, and the scene context information, using images of the scene. To predict a future path for an agent, both physical and social information must be leveraged. Previous work has not been successful to jointly model physical and social interactions. Our approach blends a social attention mechanism with a physical attention that helps the model to learn where to look in a large scene and extract the most salient parts of the image relevant to the path. Whereas, the social attention component aggregates information across the different agent interactions and extracts the most important trajectory information from the surrounding neighbors. SoPhie also takes advantage of GAN to generates more realistic samples and to capture the uncertain nature of the future paths by modeling its distribution. All these mechanisms enable our approach to predict socially and physically plausible paths for the agents and to achieve state-of-the-art performance on several different trajectory forecasting benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge