Social-BiGAT: Multimodal Trajectory Forecasting using Bicycle-GAN and Graph Attention Networks
Paper and Code
Jul 17, 2019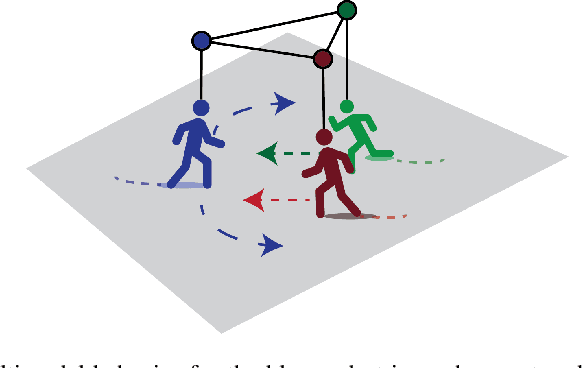
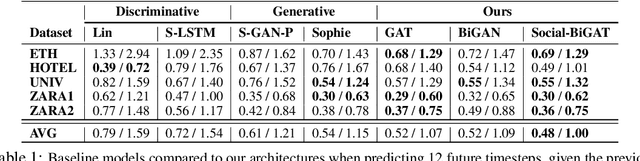
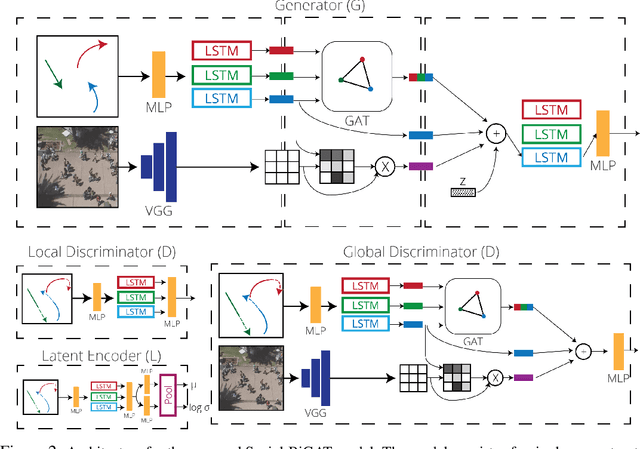
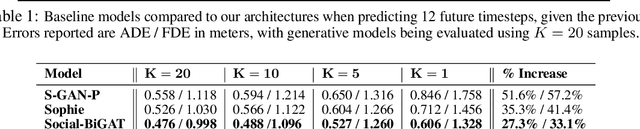
Predicting the future trajectories of multiple interacting agents in a scene has become an increasingly important problem for many different applications ranging from control of autonomous vehicles and social robots to security and surveillance. This problem is compounded by the presence of social interactions between humans and their physical interactions with the scene. While the existing literature has explored some of these cues, they mainly ignored the multimodal nature of each human's future trajectory. In this paper, we present Social-BiGAT, a graph-based generative adversarial network that generates realistic, multimodal trajectory predictions by better modelling the social interactions of pedestrians in a scene. Our method is based on a graph attention network (GAT) that learns reliable feature representations that encode the social interactions between humans in the scene, and a recurrent encoder-decoder architecture that is trained adversarially to predict, based on the features, the humans' paths. We explicitly account for the multimodal nature of the prediction problem by forming a reversible transformation between each scene and its latent noise vector, as in Bicycle-GAN. We show that our framework achieves state-of-the-art performance comparing it to several baselines on existing trajectory forecasting benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge