SLAMSpoof: Practical LiDAR Spoofing Attacks on Localization Systems Guided by Scan Matching Vulnerability Analysis
Paper and Code
Feb 19, 2025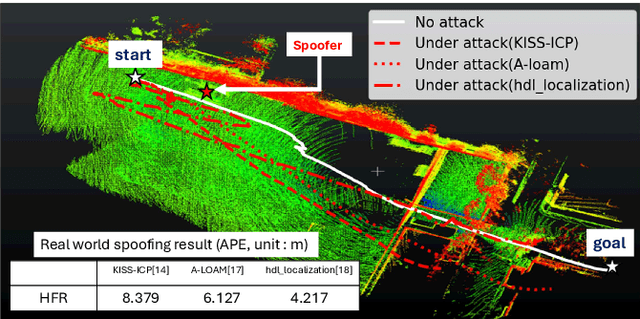

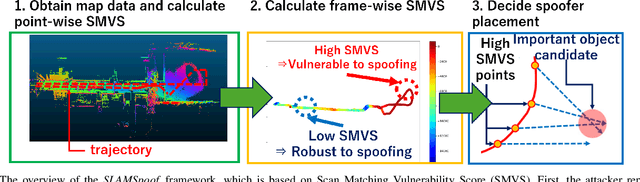
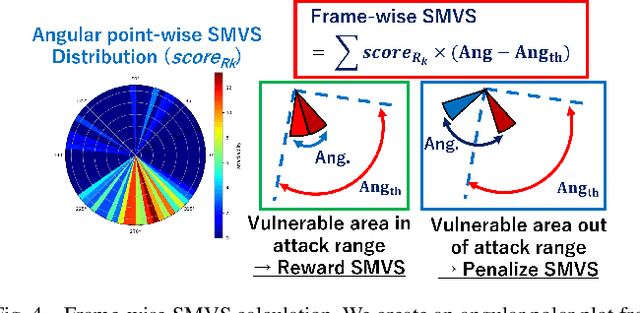
Accurate localization is essential for enabling modern full self-driving services. These services heavily rely on map-based traffic information to reduce uncertainties in recognizing lane shapes, traffic light locations, and traffic signs. Achieving this level of reliance on map information requires centimeter-level localization accuracy, which is currently only achievable with LiDAR sensors. However, LiDAR is known to be vulnerable to spoofing attacks that emit malicious lasers against LiDAR to overwrite its measurements. Once localization is compromised, the attack could lead the victim off roads or make them ignore traffic lights. Motivated by these serious safety implications, we design SLAMSpoof, the first practical LiDAR spoofing attack on localization systems for self-driving to assess the actual attack significance on autonomous vehicles. SLAMSpoof can effectively find the effective attack location based on our scan matching vulnerability score (SMVS), a point-wise metric representing the potential vulnerability to spoofing attacks. To evaluate the effectiveness of the attack, we conduct real-world experiments on ground vehicles and confirm its high capability in real-world scenarios, inducing position errors of $\geq$4.2 meters (more than typical lane width) for all 3 popular LiDAR-based localization algorithms. We finally discuss the potential countermeasures of this attack. Code is available at https://github.com/Keio-CSG/slamspoof
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge