SD-LayerNet: Semi-supervised retinal layer segmentation in OCT using disentangled representation with anatomical priors
Paper and Code
Jul 01, 2022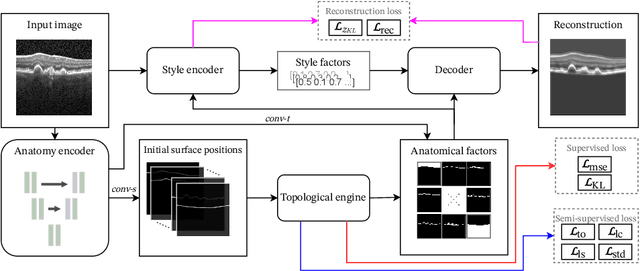
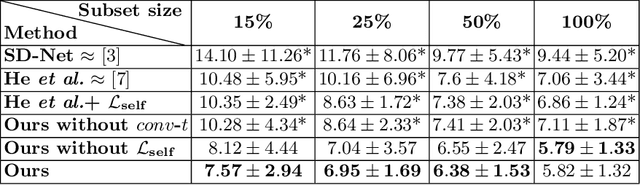
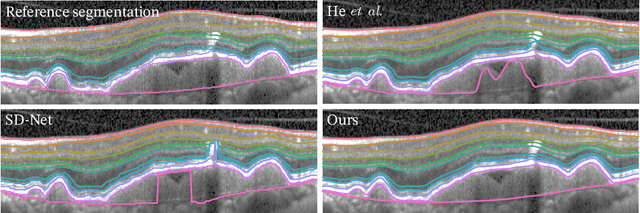
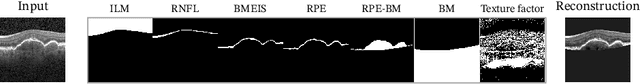
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive 3D modality widely used in ophthalmology for imaging the retina. Achieving automated, anatomically coherent retinal layer segmentation on OCT is important for the detection and monitoring of different retinal diseases, like Age-related Macular Disease (AMD) or Diabetic Retinopathy. However, the majority of state-of-the-art layer segmentation methods are based on purely supervised deep-learning, requiring a large amount of pixel-level annotated data that is expensive and hard to obtain. With this in mind, we introduce a semi-supervised paradigm into the retinal layer segmentation task that makes use of the information present in large-scale unlabeled datasets as well as anatomical priors. In particular, a novel fully differentiable approach is used for converting surface position regression into a pixel-wise structured segmentation, allowing to use both 1D surface and 2D layer representations in a coupled fashion to train the model. In particular, these 2D segmentations are used as anatomical factors that, together with learned style factors, compose disentangled representations used for reconstructing the input image. In parallel, we propose a set of anatomical priors to improve network training when a limited amount of labeled data is available. We demonstrate on the real-world dataset of scans with intermediate and wet-AMD that our method outperforms state-of-the-art when using our full training set, but more importantly largely exceeds state-of-the-art when it is trained with a fraction of the labeled data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge