SAS: Self-Augmented Strategy for Language Model Pre-training
Paper and Code
Jun 14, 2021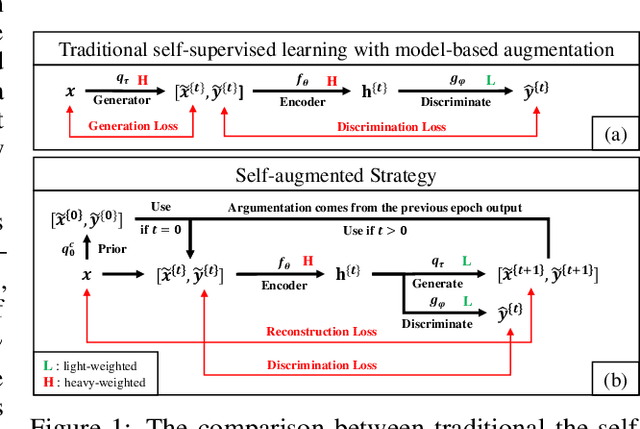
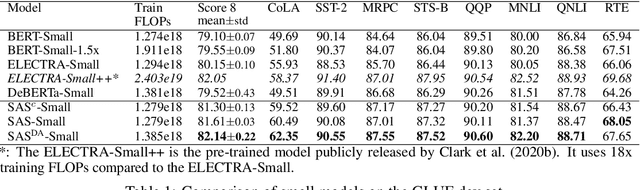
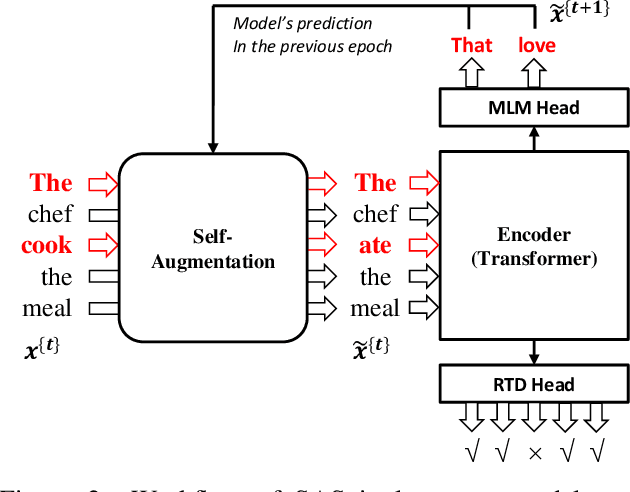
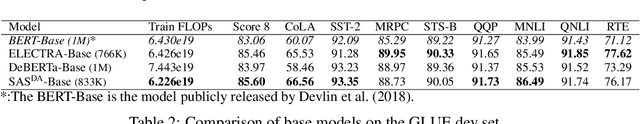
The core of a self-supervised learning method for pre-training language models includes the design of appropriate data augmentation and corresponding pre-training task(s). Most data augmentations in language model pre-training are context-independent. The seminal contextualized augmentation recently proposed by the ELECTRA requires a separate generator, which leads to extra computation cost as well as the challenge in adjusting the capability of its generator relative to that of the other model component(s). We propose a self-augmented strategy (SAS) that uses a single forward pass through the model to augment the input data for model training in the next epoch. Essentially our strategy eliminates a separate generator network and uses only one network to generate the data augmentation and undertake two pre-training tasks (the MLM task and the RTD task) jointly, which naturally avoids the challenge in adjusting the generator's capability as well as reduces the computation cost. Additionally, our SAS is a general strategy such that it can seamlessly incorporate many new techniques emerging recently or in the future, such as the disentangled attention mechanism recently proposed by the DeBERTa model. Our experiments show that our SAS is able to outperform the ELECTRA and other state-of-the-art models in the GLUE tasks with the same or less computation cost.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge