RecGURU: Adversarial Learning of Generalized User Representations for Cross-Domain Recommendation
Paper and Code
Nov 19, 2021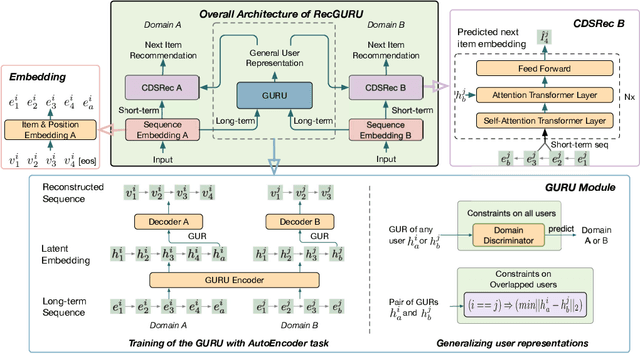
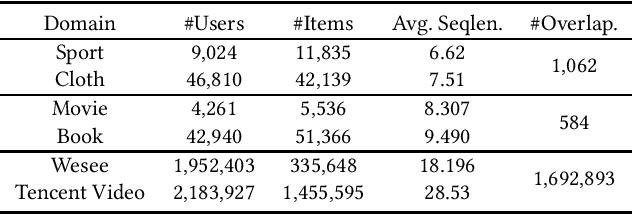
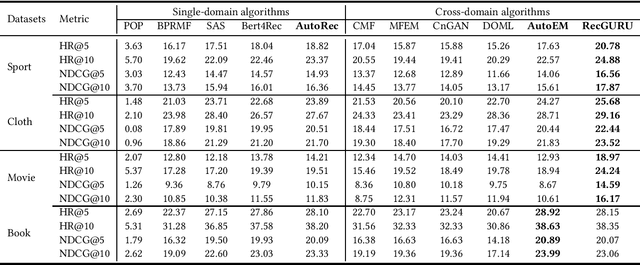
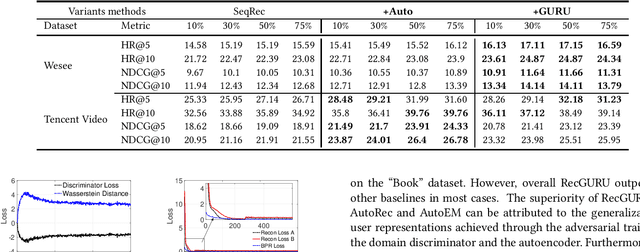
Cross-domain recommendation can help alleviate the data sparsity issue in traditional sequential recommender systems. In this paper, we propose the RecGURU algorithm framework to generate a Generalized User Representation (GUR) incorporating user information across domains in sequential recommendation, even when there is minimum or no common users in the two domains. We propose a self-attentive autoencoder to derive latent user representations, and a domain discriminator, which aims to predict the origin domain of a generated latent representation. We propose a novel adversarial learning method to train the two modules to unify user embeddings generated from different domains into a single global GUR for each user. The learned GUR captures the overall preferences and characteristics of a user and thus can be used to augment the behavior data and improve recommendations in any single domain in which the user is involved. Extensive experiments have been conducted on two public cross-domain recommendation datasets as well as a large dataset collected from real-world applications. The results demonstrate that RecGURU boosts performance and outperforms various state-of-the-art sequential recommendation and cross-domain recommendation methods. The collected data will be released to facilitate future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge