Prioritized Optimal Control
Paper and Code
Oct 16, 2014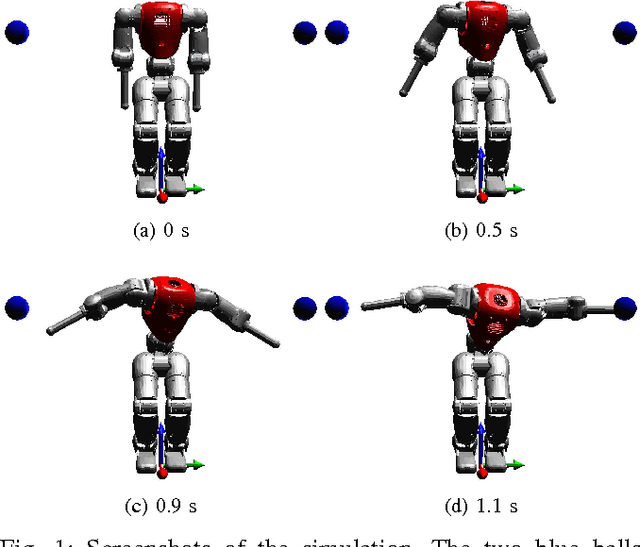



This paper presents a new technique to control highly redundant mechanical systems, such as humanoid robots. We take inspiration from two approaches. Prioritized control is a widespread multi-task technique in robotics and animation: tasks have strict priorities and they are satisfied only as long as they do not conflict with any higher-priority task. Optimal control instead formulates an optimization problem whose solution is either a feedback control policy or a feedforward trajectory of control inputs. We introduce strict priorities in multi-task optimal control problems, as an alternative to weighting task errors proportionally to their importance. This ensures the respect of the specified priorities, while avoiding numerical conditioning issues. We compared our approach with both prioritized control and optimal control with tests on a simulated robot with 11 degrees of freedom.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge