Physically-Consistent Generative Adversarial Networks for Coastal Flood Visualization
Paper and Code
May 05, 2021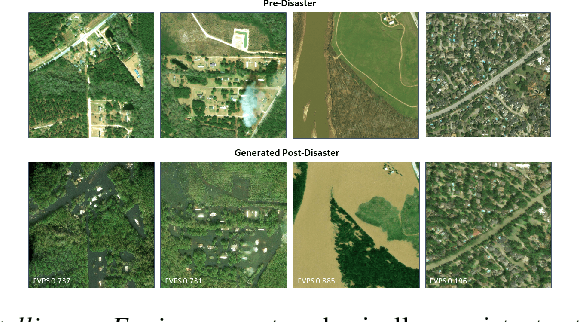
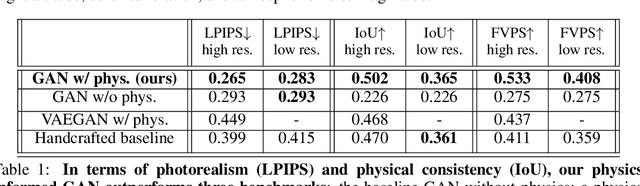
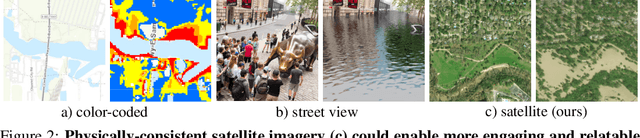
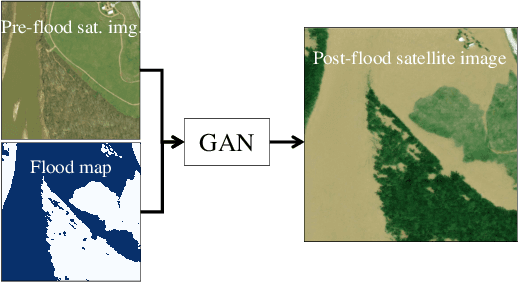
As climate change increases the intensity of natural disasters, society needs better tools for adaptation. Floods, for example, are the most frequent natural disaster, and better tools for flood risk communication could increase the support for flood-resilient infrastructure development. Our work aims to enable more visual communication of large-scale climate impacts via visualizing the output of coastal flood models as satellite imagery. We propose the first deep learning pipeline to ensure physical-consistency in synthetic visual satellite imagery. We advanced a state-of-the-art GAN called pix2pixHD, such that it produces imagery that is physically-consistent with the output of an expert-validated storm surge model (NOAA SLOSH). By evaluating the imagery relative to physics-based flood maps, we find that our proposed framework outperforms baseline models in both physical-consistency and photorealism. We envision our work to be the first step towards a global visualization of how climate change shapes our landscape. Continuing on this path, we show that the proposed pipeline generalizes to visualize arctic sea ice melt. We also publish a dataset of over 25k labelled image-pairs to study image-to-image translation in Earth observation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge