Partially-Typed NER Datasets Integration: Connecting Practice to Theory
Paper and Code
May 01, 2020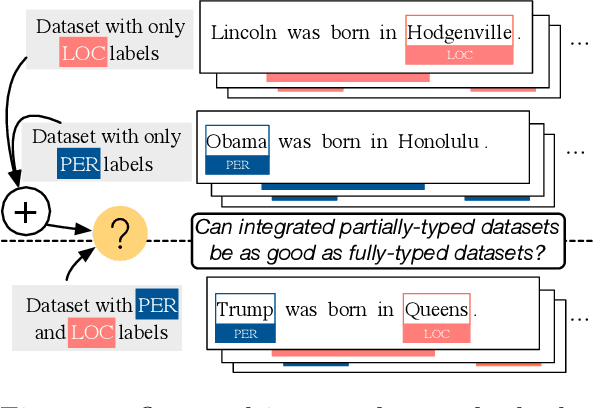
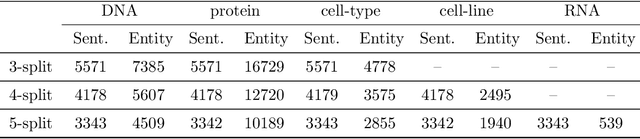


While typical named entity recognition (NER) models require the training set to be annotated with all target types, each available datasets may only cover a part of them. Instead of relying on fully-typed NER datasets, many efforts have been made to leverage multiple partially-typed ones for training and allow the resulting model to cover a full type set. However, there is neither guarantee on the quality of integrated datasets, nor guidance on the design of training algorithms. Here, we conduct a systematic analysis and comparison between partially-typed NER datasets and fully-typed ones, in both theoretical and empirical manner. Firstly, we derive a bound to establish that models trained with partially-typed annotations can reach a similar performance with the ones trained with fully-typed annotations, which also provides guidance on the algorithm design. Moreover, we conduct controlled experiments, which shows partially-typed datasets leads to similar performance with the model trained with the same amount of fully-typed annotations
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge