On the Adversarial Robustness of Learning-based Image Compression Against Rate-Distortion Attacks
Paper and Code
May 13, 2024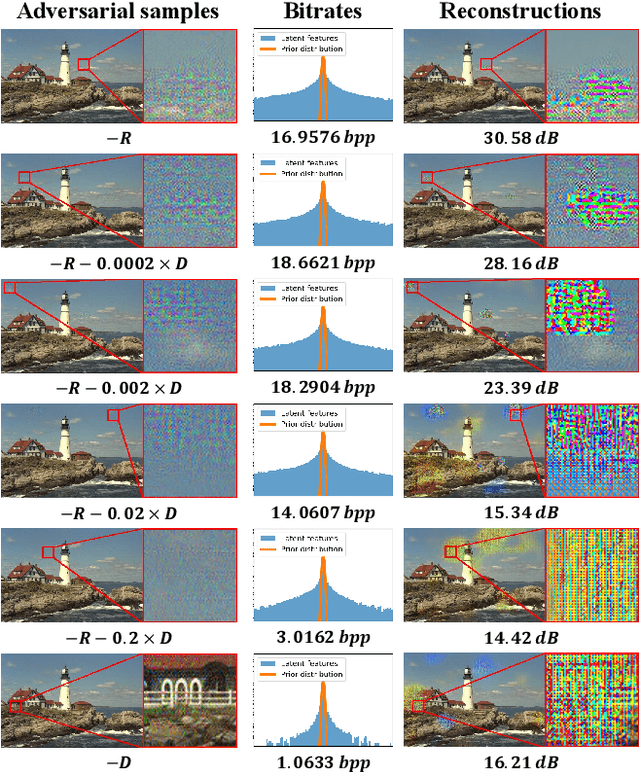
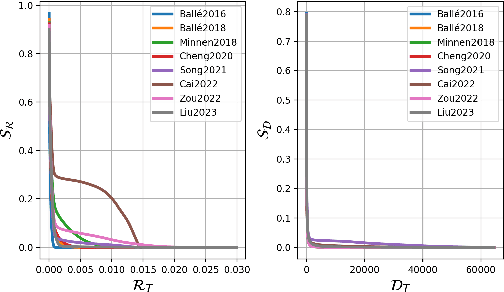


Despite demonstrating superior rate-distortion (RD) performance, learning-based image compression (LIC) algorithms have been found to be vulnerable to malicious perturbations in recent studies. Adversarial samples in these studies are designed to attack only one dimension of either bitrate or distortion, targeting a submodel with a specific compression ratio. However, adversaries in real-world scenarios are neither confined to singular dimensional attacks nor always have control over compression ratios. This variability highlights the inadequacy of existing research in comprehensively assessing the adversarial robustness of LIC algorithms in practical applications. To tackle this issue, this paper presents two joint rate-distortion attack paradigms at both submodel and algorithm levels, i.e., Specific-ratio Rate-Distortion Attack (SRDA) and Agnostic-ratio Rate-Distortion Attack (ARDA). Additionally, a suite of multi-granularity assessment tools is introduced to evaluate the attack results from various perspectives. On this basis, extensive experiments on eight prominent LIC algorithms are conducted to offer a thorough analysis of their inherent vulnerabilities. Furthermore, we explore the efficacy of two defense techniques in improving the performance under joint rate-distortion attacks. The findings from these experiments can provide a valuable reference for the development of compression algorithms with enhanced adversarial robustness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge