Network Clustering for Multi-task Learning
Paper and Code
Jan 22, 2021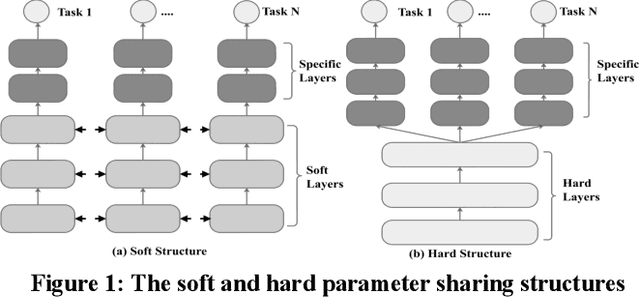
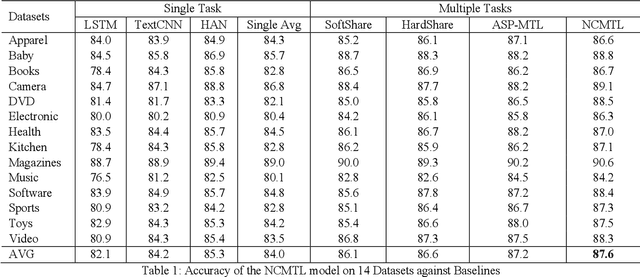
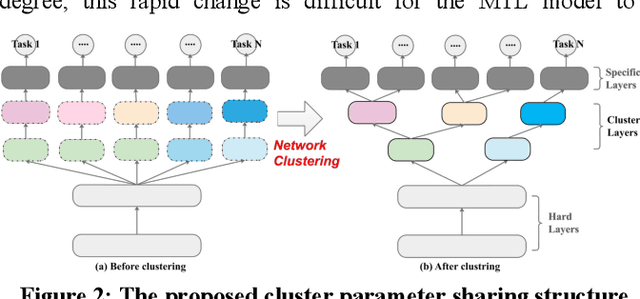
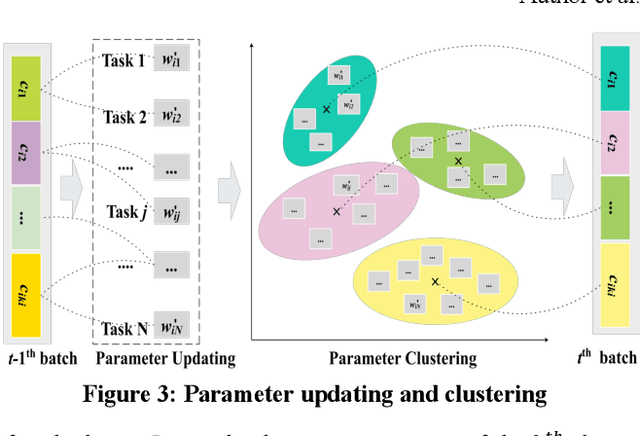
The Multi-Task Learning (MTL) technique has been widely studied by word-wide researchers. The majority of current MTL studies adopt the hard parameter sharing structure, where hard layers tend to learn general representations over all tasks and specific layers are prone to learn specific representations for each task. Since the specific layers directly follow the hard layers, the MTL model needs to estimate this direct change (from general to specific) as well. To alleviate this problem, we introduce the novel cluster layer, which groups tasks into clusters during training procedures. In a cluster layer, the tasks in the same cluster are further required to share the same network. By this way, the cluster layer produces the general presentation for the same cluster, while produces relatively specific presentations for different clusters. As transitions the cluster layers are used between the hard layers and the specific layers. The MTL model thus learns general representations to specific representations gradually. We evaluate our model with MTL document classification and the results demonstrate the cluster layer is quite efficient in MTL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge