MuSE-ing on the Impact of Utterance Ordering On Crowdsourced Emotion Annotations
Paper and Code
Mar 27, 2019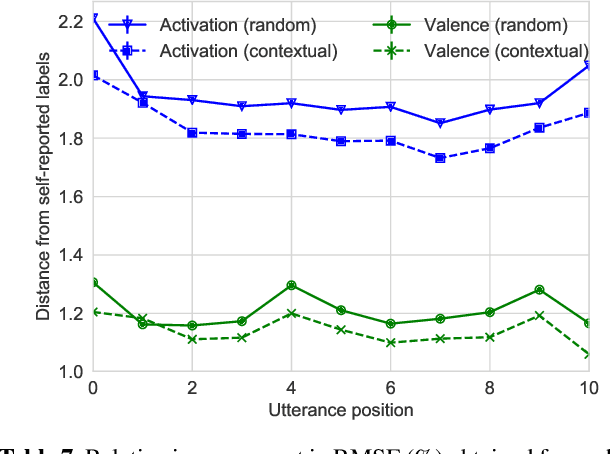
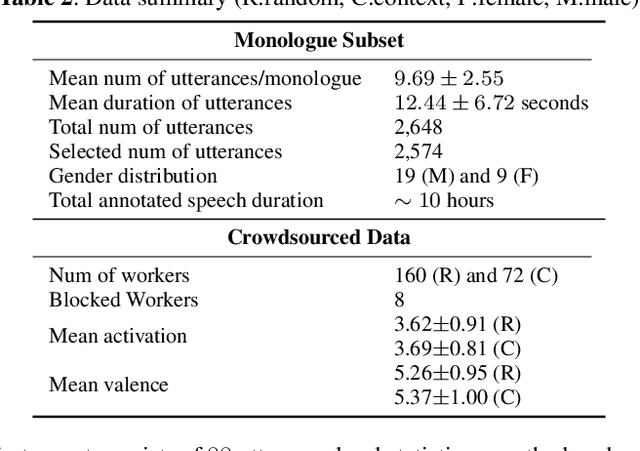
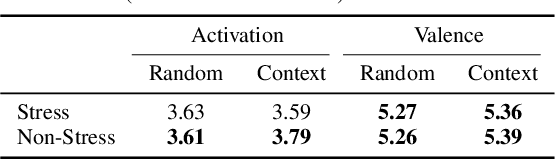
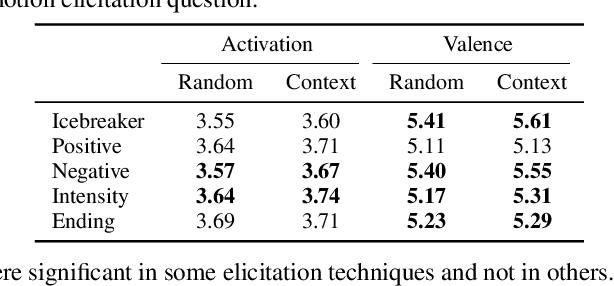
Emotion recognition algorithms rely on data annotated with high quality labels. However, emotion expression and perception are inherently subjective. There is generally not a single annotation that can be unambiguously declared "correct". As a result, annotations are colored by the manner in which they were collected. In this paper, we conduct crowdsourcing experiments to investigate this impact on both the annotations themselves and on the performance of these algorithms. We focus on one critical question: the effect of context. We present a new emotion dataset, Multimodal Stressed Emotion (MuSE), and annotate the dataset using two conditions: randomized, in which annotators are presented with clips in random order, and contextualized, in which annotators are presented with clips in order. We find that contextual labeling schemes result in annotations that are more similar to a speaker's own self-reported labels and that labels generated from randomized schemes are most easily predictable by automated systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge