Multi-level graph learning for audio event classification and human-perceived annoyance rating prediction
Paper and Code
Dec 15, 2023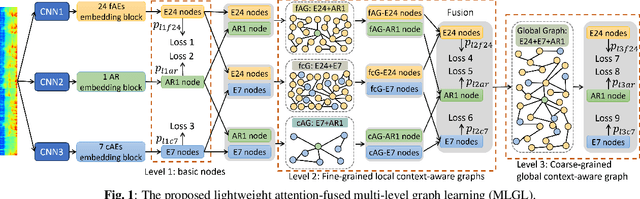
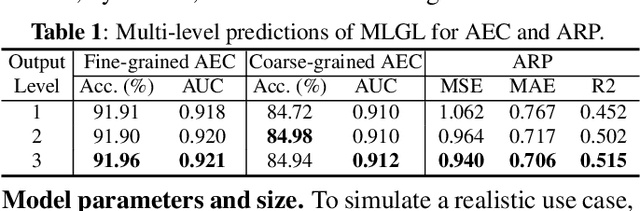
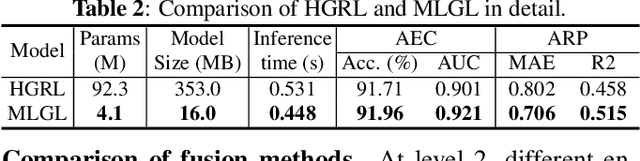
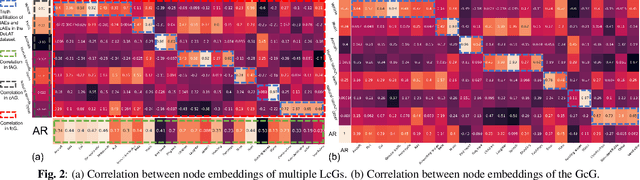
WHO's report on environmental noise estimates that 22 M people suffer from chronic annoyance related to noise caused by audio events (AEs) from various sources. Annoyance may lead to health issues and adverse effects on metabolic and cognitive systems. In cities, monitoring noise levels does not provide insights into noticeable AEs, let alone their relations to annoyance. To create annoyance-related monitoring, this paper proposes a graph-based model to identify AEs in a soundscape, and explore relations between diverse AEs and human-perceived annoyance rating (AR). Specifically, this paper proposes a lightweight multi-level graph learning (MLGL) based on local and global semantic graphs to simultaneously perform audio event classification (AEC) and human annoyance rating prediction (ARP). Experiments show that: 1) MLGL with 4.1 M parameters improves AEC and ARP results by using semantic node information in local and global context aware graphs; 2) MLGL captures relations between coarse and fine-grained AEs and AR well; 3) Statistical analysis of MLGL results shows that some AEs from different sources significantly correlate with AR, which is consistent with previous research on human perception of these sound sources.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge