MiM: Mask in Mask Self-Supervised Pre-Training for 3D Medical Image Analysis
Paper and Code
Apr 24, 2024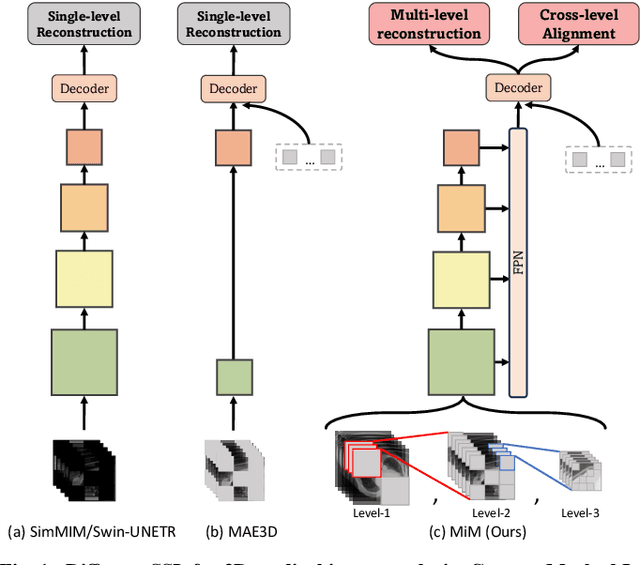
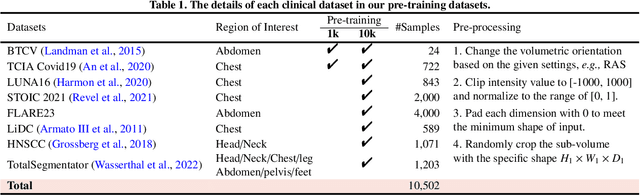
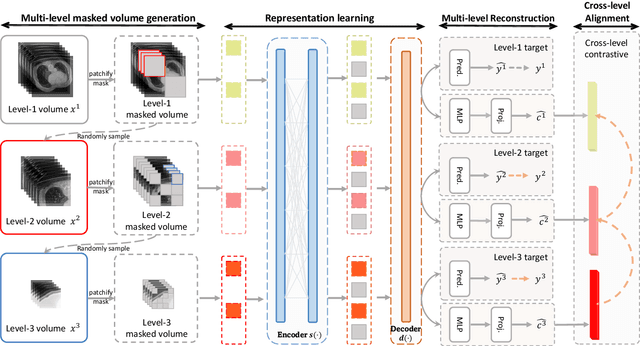
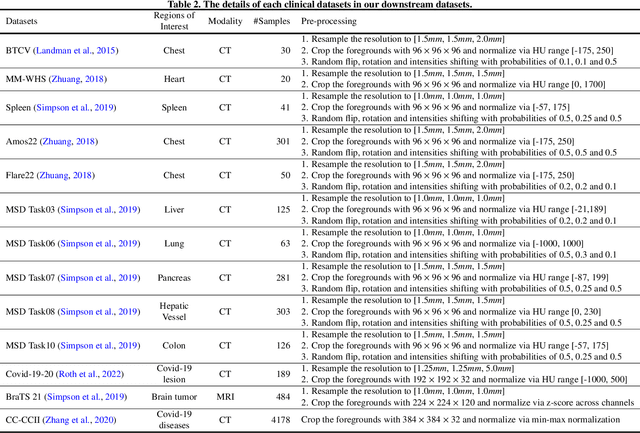
The Vision Transformer (ViT) has demonstrated remarkable performance in Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) for 3D medical image analysis. Mask AutoEncoder (MAE) for feature pre-training can further unleash the potential of ViT on various medical vision tasks. However, due to large spatial sizes with much higher dimensions of 3D medical images, the lack of hierarchical design for MAE may hinder the performance of downstream tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel \textit{Mask in Mask (MiM)} pre-training framework for 3D medical images, which aims to advance MAE by learning discriminative representation from hierarchical visual tokens across varying scales. We introduce multiple levels of granularity for masked inputs from the volume, which are then reconstructed simultaneously ranging at both fine and coarse levels. Additionally, a cross-level alignment mechanism is applied to adjacent level volumes to enforce anatomical similarity hierarchically. Furthermore, we adopt a hybrid backbone to enhance the hierarchical representation learning efficiently during the pre-training. MiM was pre-trained on a large scale of available 3D volumetric images, \textit{i.e.,} Computed Tomography (CT) images containing various body parts. Extensive experiments on thirteen public datasets demonstrate the superiority of MiM over other SSL methods in organ/lesion/tumor segmentation and disease classification. We further scale up the MiM to large pre-training datasets with more than 10k volumes, showing that large-scale pre-training can further enhance the performance of downstream tasks. The improvement also concluded that the research community should pay more attention to the scale of the pre-training dataset towards the healthcare foundation model for 3D medical images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge