Look Twice Before You Answer: Memory-Space Visual Retracing for Hallucination Mitigation in Multimodal Large Language Models
Paper and Code
Oct 04, 2024
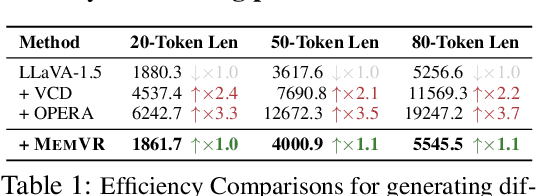
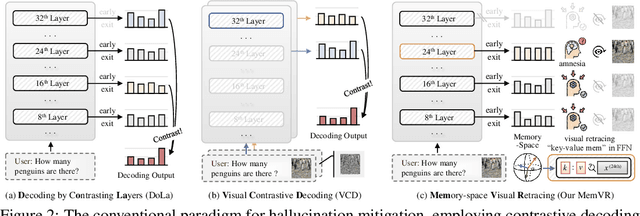
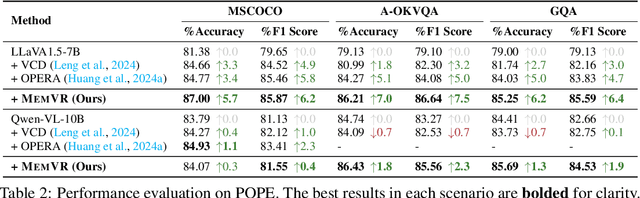
Despite their impressive capabilities, Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) are susceptible to hallucinations, especially assertively fabricating content not present in the visual inputs. To address the aforementioned challenge, we follow a common cognitive process - when one's initial memory of critical on-sight details fades, it is intuitive to look at them a second time to seek a factual and accurate answer. Therefore, we introduce Memory-space Visual Retracing (MemVR), a novel hallucination mitigation paradigm that without the need for external knowledge retrieval or additional fine-tuning. In particular, we treat visual prompts as supplementary evidence to be reinjected into MLLMs via Feed Forward Network (FFN) as key-value memory, when the model is uncertain or even amnesic about question-relevant visual memories. Comprehensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that MemVR significantly mitigates hallucination issues across various MLLMs and excels in general benchmarks without incurring added time overhead, thus emphasizing its potential for widespread applicability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge