Learning to Rank Query Graphs for Complex Question Answering over Knowledge Graphs
Paper and Code
Nov 02, 2018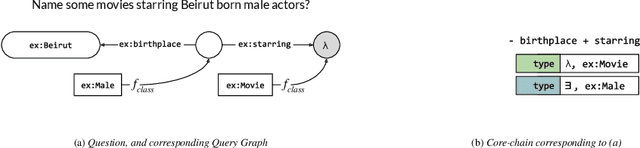
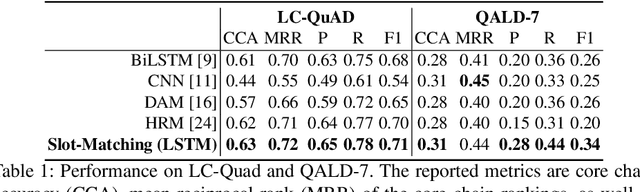
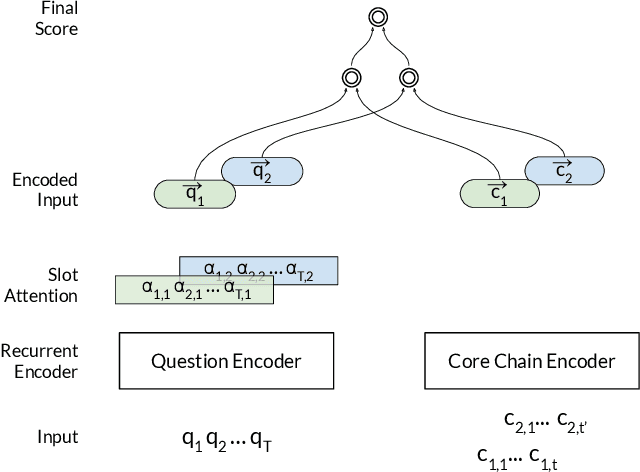
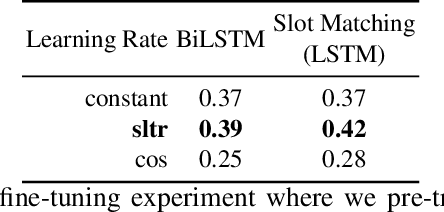
In this paper, we conduct an empirical investigation of neural query graph ranking approaches for the task of complex question answering over knowledge graphs. We experiment with six different ranking models and propose a novel self-attention based slot matching model which exploits the inherent structure of query graphs, our logical form of choice. Our proposed model generally outperforms the other models on two QA datasets over the DBpedia knowledge graph, evaluated in different settings. In addition, we show that transfer learning from the larger of those QA datasets to the smaller dataset yields substantial improvements, effectively offsetting the general lack of training data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge