Learnable Prompt as Pseudo-Imputation: Reassessing the Necessity of Traditional EHR Data Imputation in Downstream Clinical Prediction
Paper and Code
Jan 30, 2024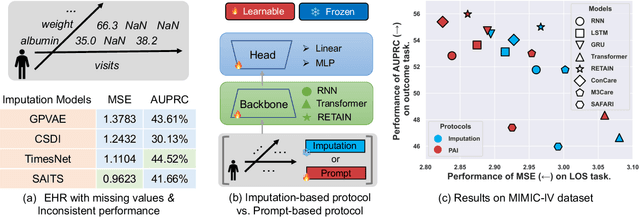
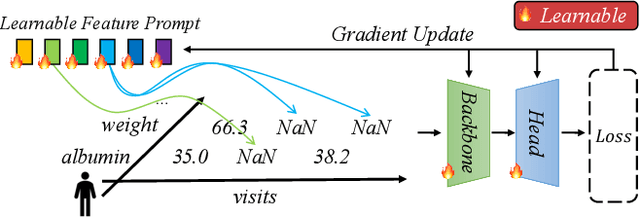
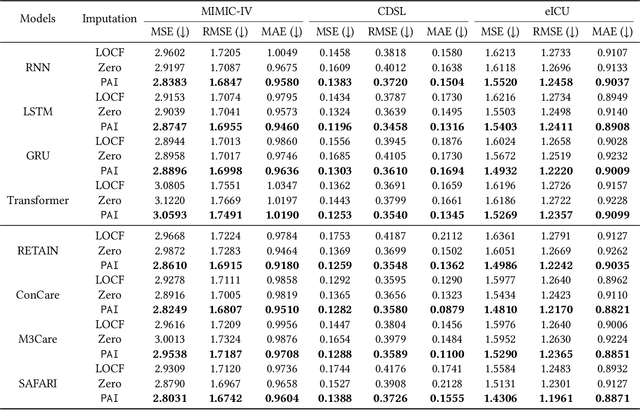
Analyzing the health status of patients based on Electronic Health Records (EHR) is a fundamental research problem in medical informatics. The presence of extensive missing values in EHR makes it challenging for deep neural networks to directly model the patient's health status based on EHR. Existing deep learning training protocols require the use of statistical information or imputation models to reconstruct missing values; however, the protocols inject non-realistic data into downstream EHR analysis models, significantly limiting model performance. This paper introduces Learnable Prompt as Pseudo Imputation (PAI) as a new training protocol. PAI no longer introduces any imputed data but constructs a learnable prompt to model the implicit preferences of the downstream model for missing values, resulting in a significant performance improvement for all EHR analysis models. Additionally, our experiments show that PAI exhibits higher robustness in situations of data insufficiency and high missing rates. More importantly, in a real-world application involving cross-institutional data with zero-shot evaluation, PAI demonstrates stronger model generalization capabilities for non-overlapping features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge