Investigating Stateful Defenses Against Black-Box Adversarial Examples
Paper and Code
Mar 17, 2023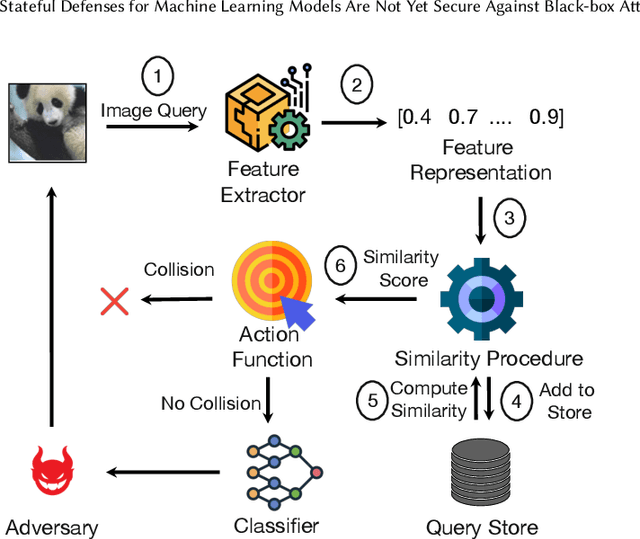

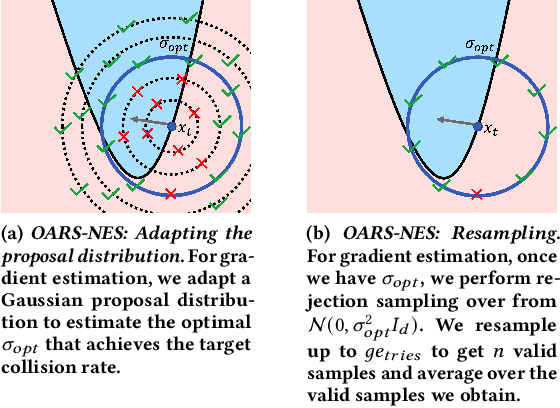
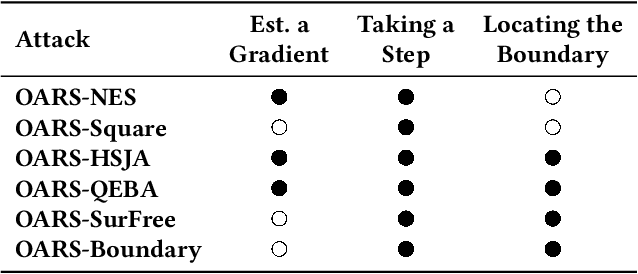
Defending machine-learning (ML) models against white-box adversarial attacks has proven to be extremely difficult. Instead, recent work has proposed stateful defenses in an attempt to defend against a more restricted black-box attacker. These defenses operate by tracking a history of incoming model queries, and rejecting those that are suspiciously similar. The current state-of-the-art stateful defense Blacklight was proposed at USENIX Security '22 and claims to prevent nearly 100% of attacks on both the CIFAR10 and ImageNet datasets. In this paper, we observe that an attacker can significantly reduce the accuracy of a Blacklight-protected classifier (e.g., from 82.2% to 6.4% on CIFAR10) by simply adjusting the parameters of an existing black-box attack. Motivated by this surprising observation, since existing attacks were evaluated by the Blacklight authors, we provide a systematization of stateful defenses to understand why existing stateful defense models fail. Finally, we propose a stronger evaluation strategy for stateful defenses comprised of adaptive score and hard-label based black-box attacks. We use these attacks to successfully reduce even reconfigured versions of Blacklight to as low as 0% robust accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge