Internal language model estimation through explicit context vector learning for attention-based encoder-decoder ASR
Paper and Code
Jan 26, 2022
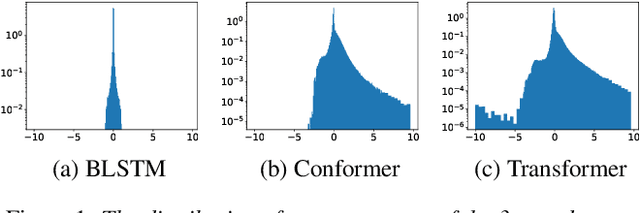
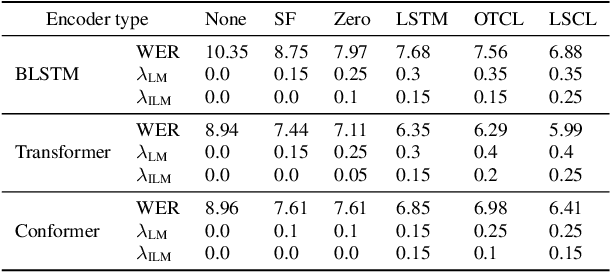
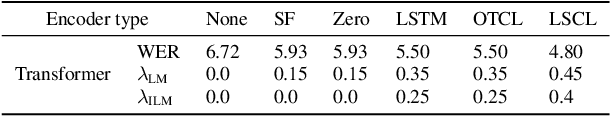
An end-to-end (E2E) speech recognition model implicitly learns a biased internal language model (ILM) during training. To fused an external LM during inference, the scores produced by the biased ILM need to be estimated and subtracted. In this paper we propose two novel approaches to estimate the biased ILM based on Listen-Attend-Spell (LAS) models. The simpler method is to replace the context vector of the LAS decoder at every time step with a learnable vector. The other more advanced method is to use a simple feed-forward network to directly map query vectors to context vectors, making the generation of the context vectors independent of the LAS encoder. Both the learnable vector and the mapping network are trained on the transcriptions of the training data to minimize the perplexity while all the other parameters of the LAS model is fixed. Experiments show that the ILMs estimated by the proposed methods achieve the lowest perplexity. In addition, they also significantly outperform the shallow fusion method and two previously proposed Internal Language Model Estimation (ILME) approaches on multiple datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge