Interactive Hand Pose Estimation: Boosting accuracy in localizing extended finger joints
Paper and Code
Jul 25, 2018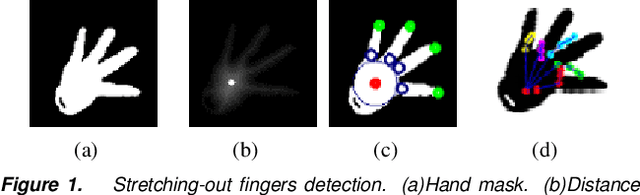
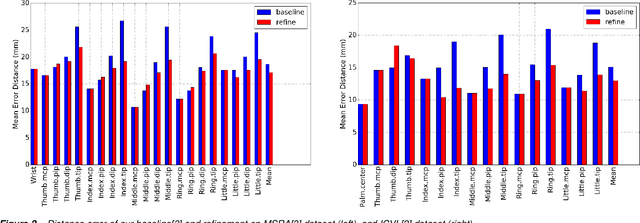
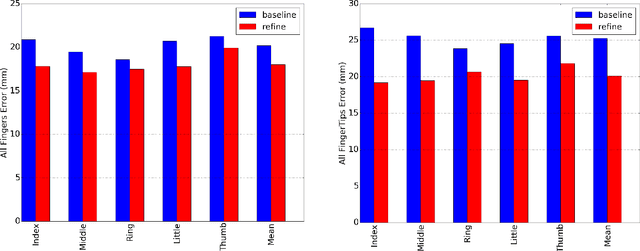
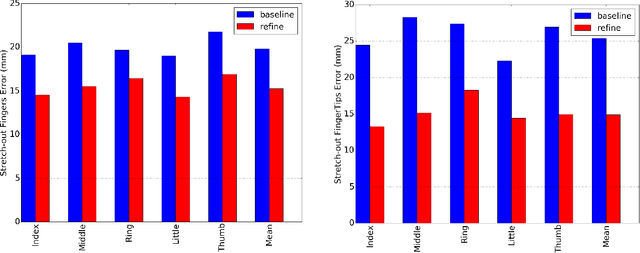
Accurate 3D hand pose estimation plays an important role in Human Machine Interaction (HMI). In the reality of HMI, joints in fingers stretching out, especially corresponding fingertips, are much more important than other joints. We propose a novel method to refine stretching-out finger joint locations after obtaining rough hand pose estimation. It first detects which fingers are stretching out, then neighbor pixels of certain joint vote for its new location based on random forests. The algorithm is tested on two public datasets: MSRA15 and ICVL. After the refinement stage of stretching-out fingers, errors of predicted HMI finger joint locations are significantly reduced. Mean error of all fingertips reduces around 5mm (relatively more than 20%). Stretching-out fingertip locations are even more precise, which in MSRA15 reduces 10.51mm (relatively 41.4%).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge