Improving Factual Consistency of Text Summarization by Adversarially Decoupling Comprehension and Embellishment Abilities of LLMs
Paper and Code
Nov 01, 2023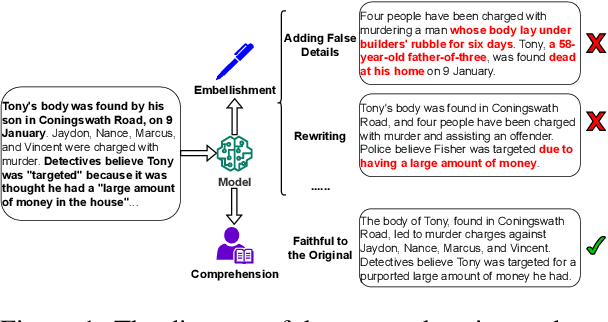
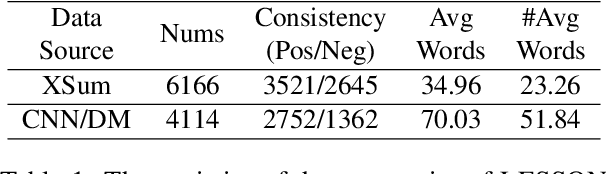
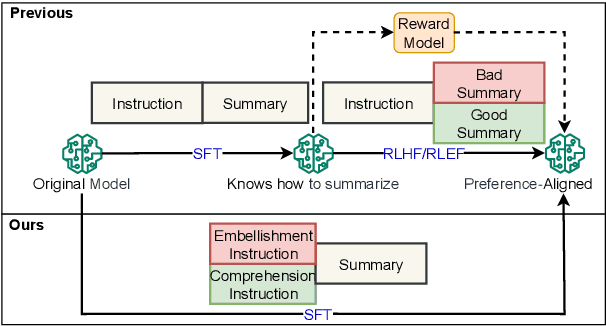
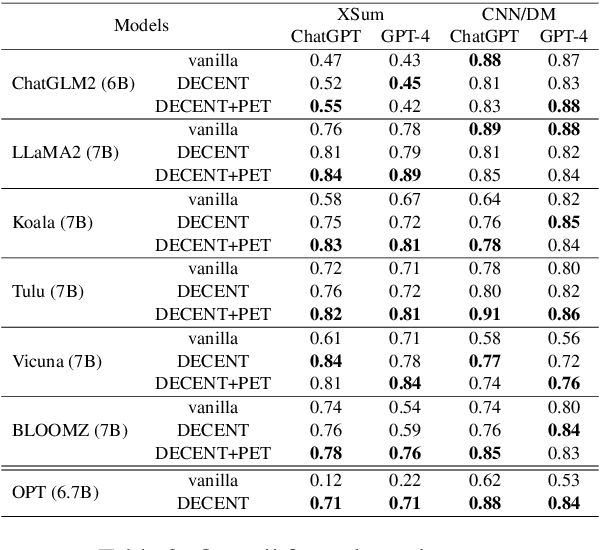
Despite the recent progress in text summarization made by large language models (LLMs), they often generate summaries that are factually inconsistent with original articles, known as "hallucinations" in text generation. Unlike previous small models (e.g., BART, T5), current LLMs make fewer silly mistakes but more sophisticated ones, such as imposing cause and effect, adding false details, and overgeneralizing, etc. These hallucinations are challenging to detect through traditional methods, which poses great challenges for improving the factual consistency of text summarization. In this paper, we propose an adversarially DEcoupling method to disentangle the Comprehension and EmbellishmeNT abilities of LLMs (DECENT). Furthermore, we adopt a probing-based parameter-efficient technique to cover the shortage of sensitivity for true and false in the training process of LLMs. In this way, LLMs are less confused about embellishing and understanding, thus can execute the instructions more accurately and have enhanced abilities to distinguish hallucinations. Experimental results show that DECENT significantly improves the reliability of text summarization based on LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge