HINT: Hierarchical Invertible Neural Transport for General and Sequential Bayesian inference
Paper and Code
May 25, 2019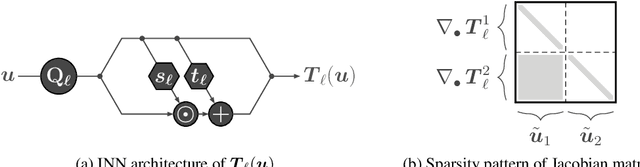
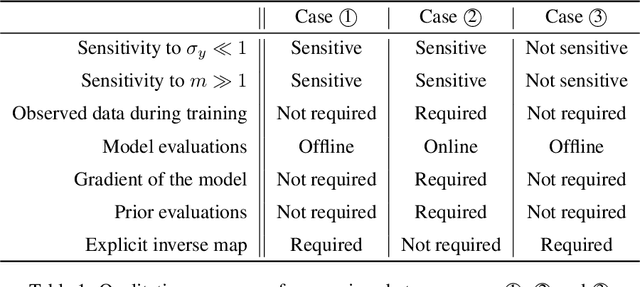
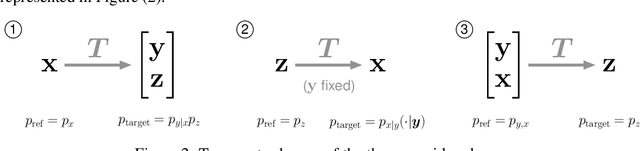
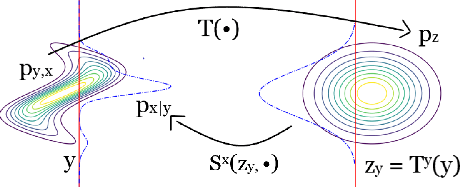
In this paper, we introduce Hierarchical Invertible Neural Transport (HINT), an algorithm that merges Invertible Neural Networks and optimal transport to sample from a posterior distribution in a Bayesian framework. This method exploits a hierarchical architecture to construct a Knothe-Rosenblatt transport map between an arbitrary density and the joint density of hidden variables and observations. After training the map, samples from the posterior can be immediately recovered for any contingent observation. Any underlying model evaluation can be performed fully offline from training without the need of a model-gradient. Furthermore, no analytical evaluation of the prior is necessary, which makes HINT an ideal candidate for sequential Bayesian inference. We demonstrate the efficacy of HINT on two numerical experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge