HI-GVF: Shared Control based on Human-Influenced Guiding Vector Fields for Human-multi-robot Cooperation
Paper and Code
Feb 17, 2025
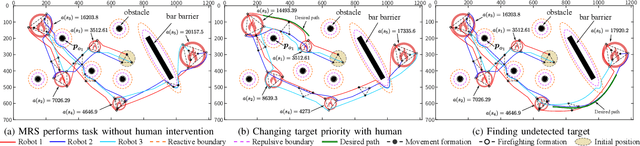
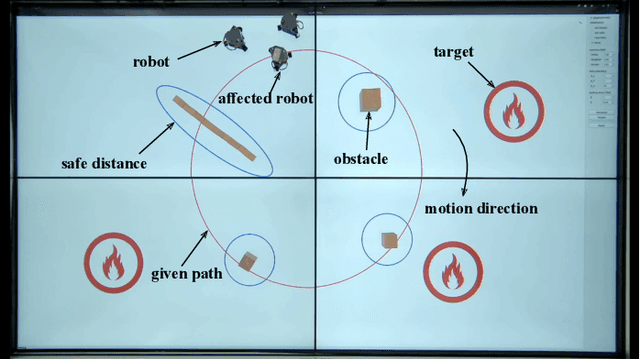
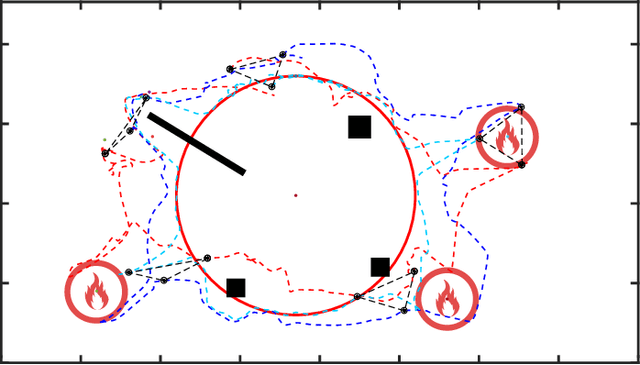
Human-multi-robot shared control leverages human decision-making and robotic autonomy to enhance human-robot collaboration. While widely studied, existing systems often adopt a leader-follower model, limiting robot autonomy to some extent. Besides, a human is required to directly participate in the motion control of robots through teleoperation, which significantly burdens the operator. To alleviate these two issues, we propose a layered shared control computing framework using human-influenced guiding vector fields (HI-GVF) for human-robot collaboration. HI-GVF guides the multi-robot system along a desired path specified by the human. Then, an intention field is designed to merge the human and robot intentions, accelerating the propagation of the human intention within the multi-robot system. Moreover, we give the stability analysis of the proposed model and use collision avoidance based on safety barrier certificates to fine-tune the velocity. Eventually, considering the firefighting task as an example scenario, we conduct simulations and experiments using multiple human-robot interfaces (brain-computer interface, myoelectric wristband, eye-tracking), and the results demonstrate that our proposed approach boosts the effectiveness and performance of the task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge