Heterogeneous Multi-agent Zero-Shot Coordination by Coevolution
Paper and Code
Aug 09, 2022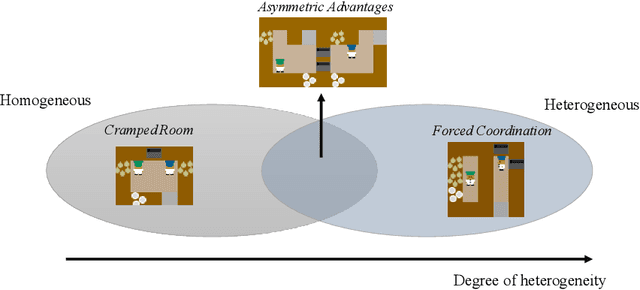
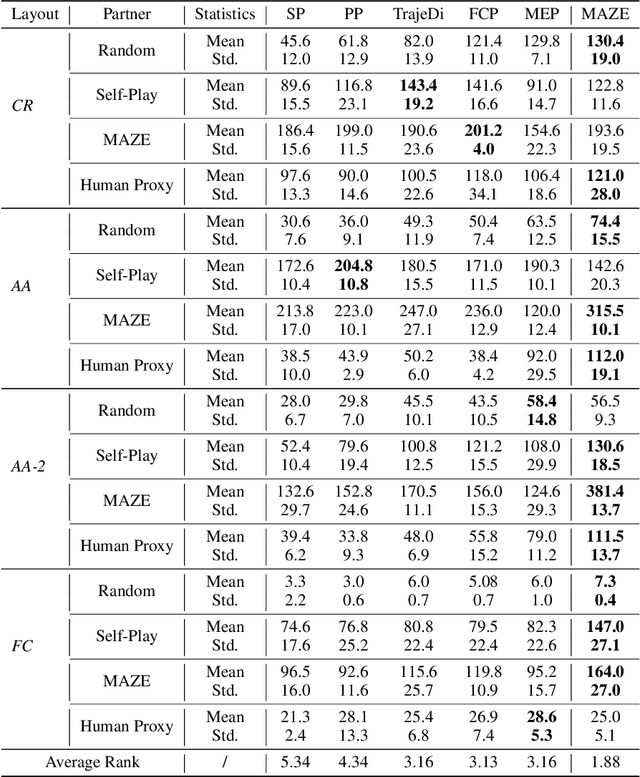

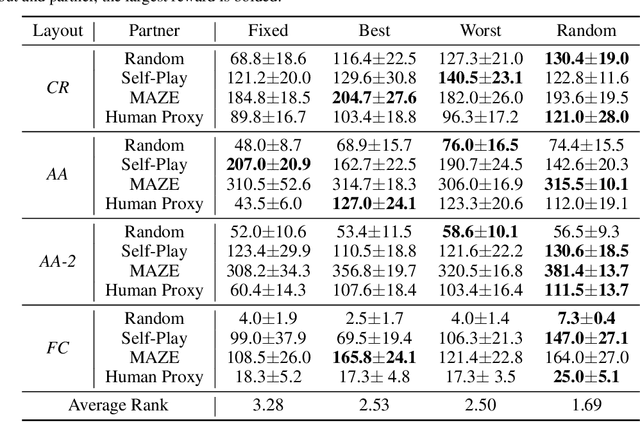
Generating agents that can achieve Zero-Shot Coordination (ZSC) with unseen partners is a new challenge in cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL). Recently, some studies have made progress in ZSC by exposing the agents to diverse partners during the training process. They usually involve self-play when training the partners, implicitly assuming that the tasks are homogeneous. However, many real-world tasks are heterogeneous, and hence previous methods may fail. In this paper, we study the heterogeneous ZSC problem for the first time and propose a general method based on coevolution, which coevolves two populations of agents and partners through three sub-processes: pairing, updating and selection. Experimental results on a collaborative cooking task show the necessity of considering the heterogeneous setting and illustrate that our proposed method is a promising solution for heterogeneous cooperative MARL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge