Harnessing the Power of Deep Learning Methods in Healthcare: Neonatal Pain Assessment from Crying Sound
Paper and Code
Sep 05, 2019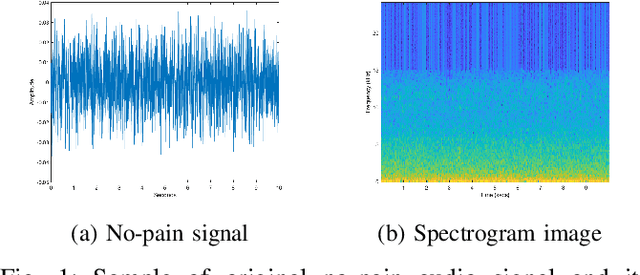
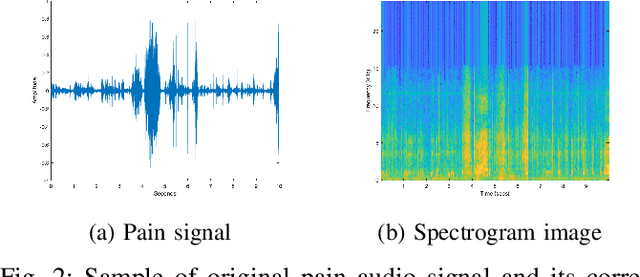
Neonatal pain assessment in clinical environments is challenging as it is discontinuous and biased. Facial/body occlusion can occur in such settings due to clinical condition, developmental delays, prone position, or other external factors. In such cases, crying sound can be used to effectively assess neonatal pain. In this paper, we investigate the use of a novel CNN architecture (N-CNN) along with other CNN architectures (VGG16 and ResNet50) for assessing pain from crying sounds of neonates. The experimental results demonstrate that using our novel N-CNN for assessing pain from the sounds of neonates has a strong clinical potential and provides a viable alternative to the current assessment practice.
* Accepted to IEEE HI-POCT 2019
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge