Generalized Label Enhancement with Sample Correlations
Paper and Code
Apr 07, 2020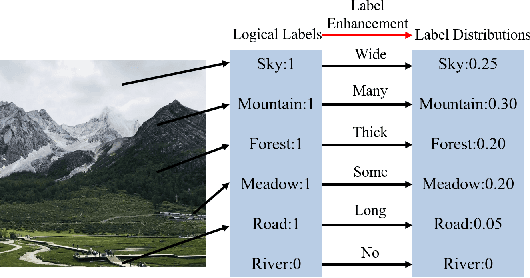
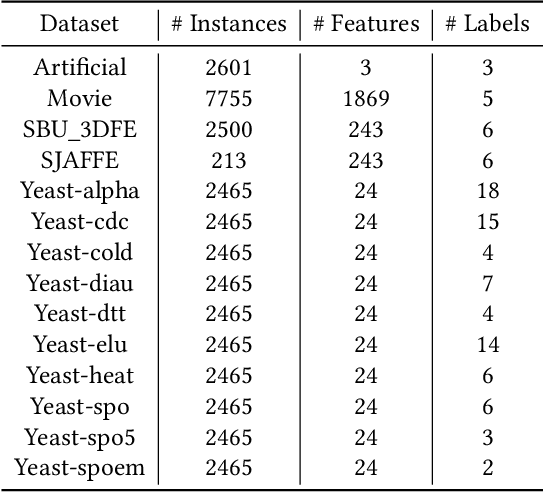
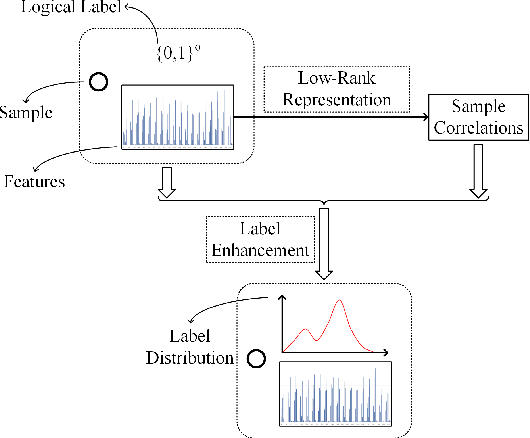
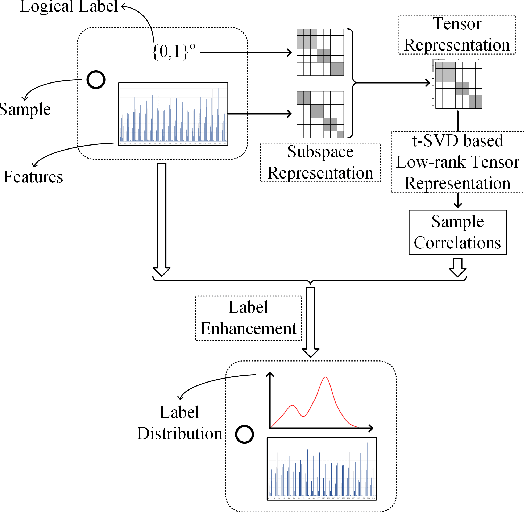
Recently, label distribution learning (LDL) has drawn much attention in machine learning, where LDL model is learned from labeled instances. Different from single-label and multi-label annotations, label distributions describe the instance by multiple labels with different intensities and accommodates to more general conditions. As most existing machine learning datasets merely provide logical labels, label distributions are unavailable in many real-world applications. To handle this problem, we propose two novel label enhancement methods, i.e., Label Enhancement with Sample Correlations (LESC) and generalized Label Enhancement with Sample Correlations (gLESC). More specifically, LESC employs a low-rank representation of samples in the feature space, and gLESC leverages a tensor multi-rank minimization to further investigate sample correlations in both the feature space and label space. Benefit from the sample correlation, the proposed method can boost the performance of LE. Extensive experiments on 14 benchmark datasets demonstrate that LESC and gLESC can achieve state-of-the-art results as compared to previous label enhancement baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge