GANet: Goal Area Network for Motion Forecasting
Paper and Code
Sep 20, 2022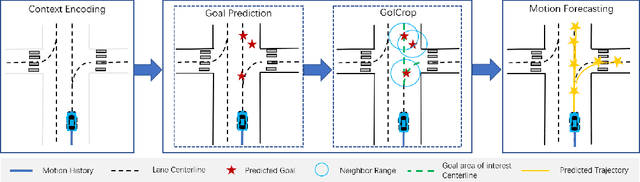
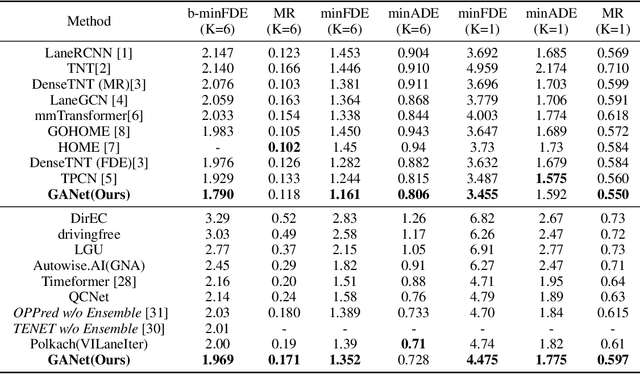
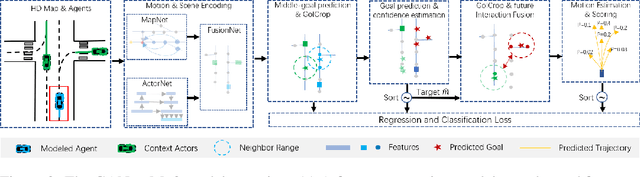
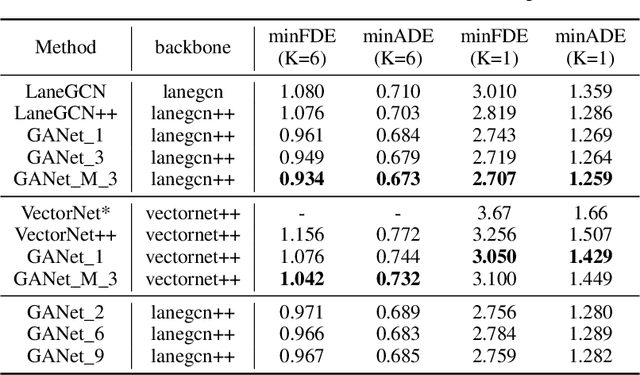
Predicting the future motion of road participants is crucial for autonomous driving but is extremely challenging due to staggering motion uncertainty. Recently, most motion forecasting methods resort to the goal-based strategy, i.e., predicting endpoints of motion trajectories as conditions to regress the entire trajectories, so that the search space of solution can be reduced. However, accurate goal coordinates are hard to predict and evaluate. In addition, the point representation of the destination limits the utilization of a rich road context, leading to inaccurate prediction results in many cases. Goal area, i.e., the possible destination area, rather than goal coordinate, could provide a more soft constraint for searching potential trajectories by involving more tolerance and guidance. In view of this, we propose a new goal area-based framework, named Goal Area Network (GANet), for motion forecasting, which models goal areas rather than exact goal coordinates as preconditions for trajectory prediction, performing more robustly and accurately. Specifically, we propose a GoICrop (Goal Area of Interest) operator to effectively extract semantic lane features in goal areas and model actors' future interactions, which benefits a lot for future trajectory estimations. GANet ranks the 1st on the leaderboard of Argoverse Challenge among all public literature (till the paper submission), and its source codes will be released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge