Explainable Object-induced Action Decision for Autonomous Vehicles
Paper and Code
Mar 20, 2020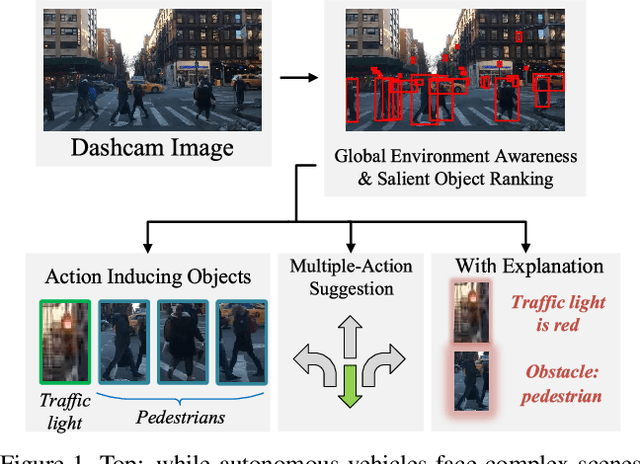
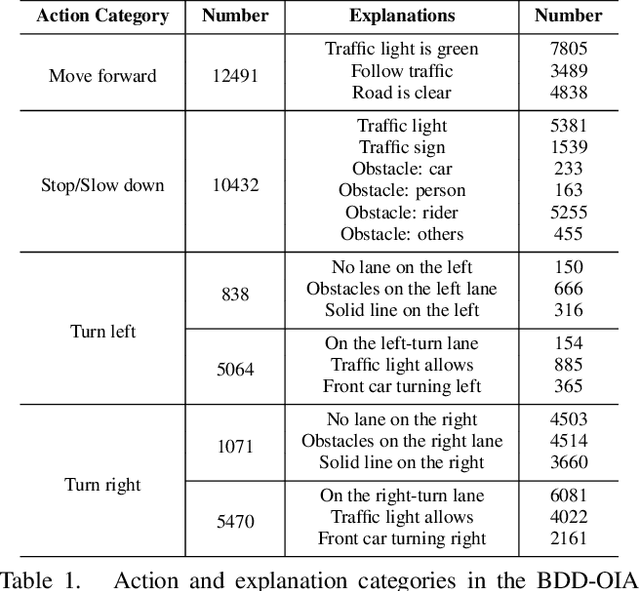
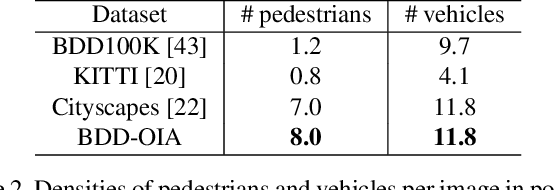

A new paradigm is proposed for autonomous driving. The new paradigm lies between the end-to-end and pipelined approaches, and is inspired by how humans solve the problem. While it relies on scene understanding, the latter only considers objects that could originate hazard. These are denoted as action-inducing, since changes in their state should trigger vehicle actions. They also define a set of explanations for these actions, which should be produced jointly with the latter. An extension of the BDD100K dataset, annotated for a set of 4 actions and 21 explanations, is proposed. A new multi-task formulation of the problem, which optimizes the accuracy of both action commands and explanations, is then introduced. A CNN architecture is finally proposed to solve this problem, by combining reasoning about action inducing objects and global scene context. Experimental results show that the requirement of explanations improves the recognition of action-inducing objects, which in turn leads to better action predictions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge