Exceeding the Maximum Speed Limit of the Joint Angle for the Redundant Tendon-driven Structures of Musculoskeletal Humanoids
Paper and Code
Feb 18, 2025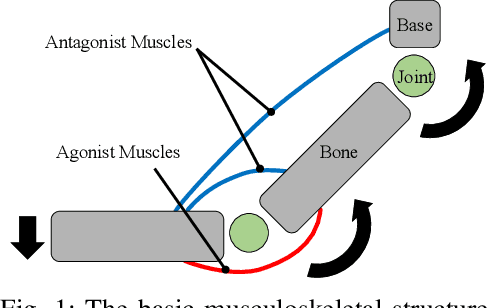
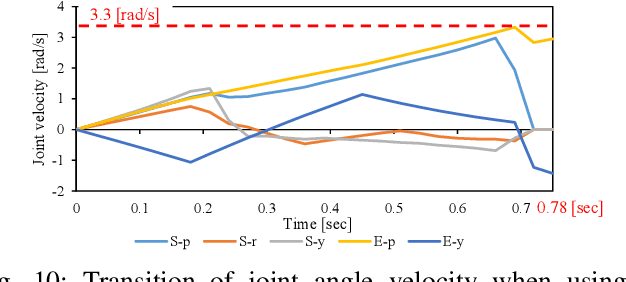
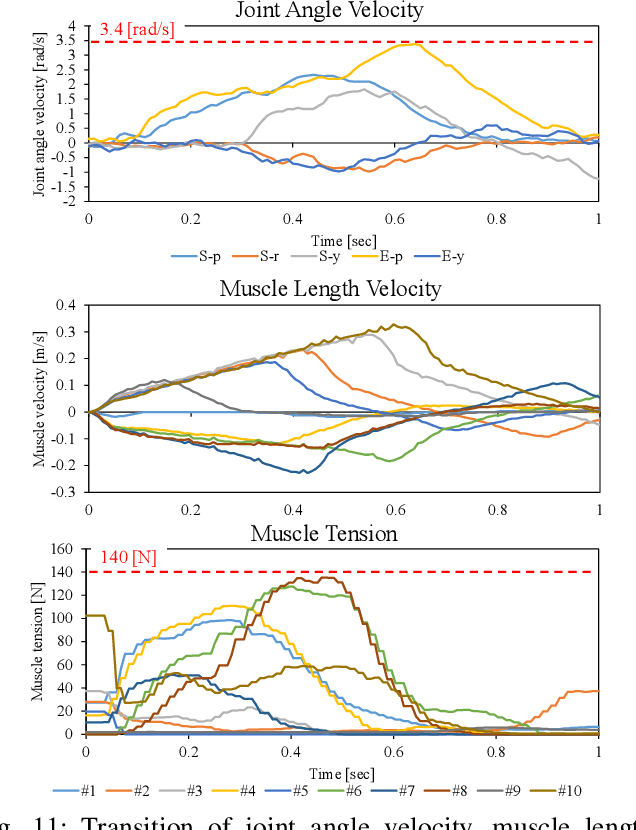
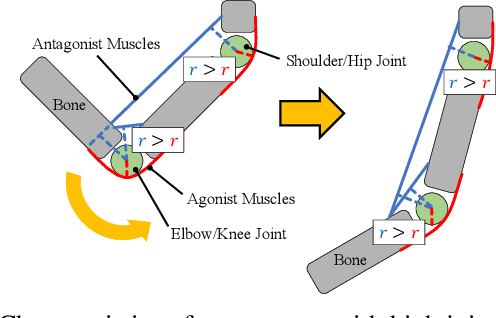
The musculoskeletal humanoid has various biomimetic benefits, and the redundant muscle arrangement is one of its most important characteristics. This redundancy can achieve fail-safe redundant actuation and variable stiffness control. However, there is a problem that the maximum joint angle velocity is limited by the slowest muscle among the redundant muscles. In this study, we propose two methods that can exceed the limited maximum joint angle velocity, and verify the effectiveness with actual robot experiments.
* Accepted at IROS2020
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge