Eventor: An Efficient Event-Based Monocular Multi-View Stereo Accelerator on FPGA Platform
Paper and Code
Mar 29, 2022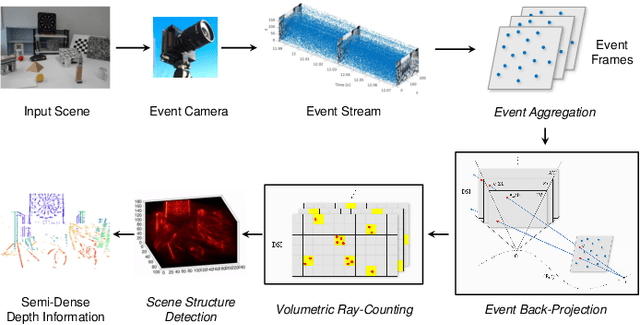
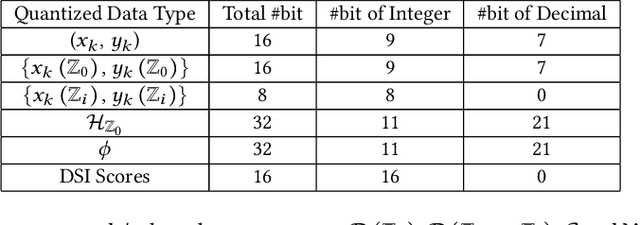
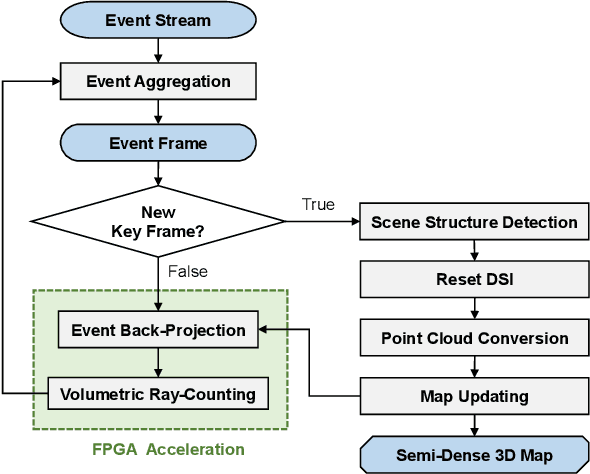
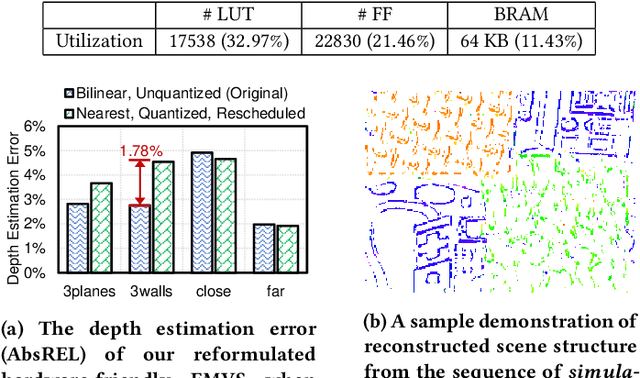
Event cameras are bio-inspired vision sensors that asynchronously represent pixel-level brightness changes as event streams. Event-based monocular multi-view stereo (EMVS) is a technique that exploits the event streams to estimate semi-dense 3D structure with known trajectory. It is a critical task for event-based monocular SLAM. However, the required intensive computation workloads make it challenging for real-time deployment on embedded platforms. In this paper, Eventor is proposed as a fast and efficient EMVS accelerator by realizing the most critical and time-consuming stages including event back-projection and volumetric ray-counting on FPGA. Highly paralleled and fully pipelined processing elements are specially designed via FPGA and integrated with the embedded ARM as a heterogeneous system to improve the throughput and reduce the memory footprint. Meanwhile, the EMVS algorithm is reformulated to a more hardware-friendly manner by rescheduling, approximate computing and hybrid data quantization. Evaluation results on DAVIS dataset show that Eventor achieves up to $24\times$ improvement in energy efficiency compared with Intel i5 CPU platform.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge