Empirical Comparison of Graph Embeddings for Trust-Based Collaborative Filtering
Paper and Code
Mar 30, 2020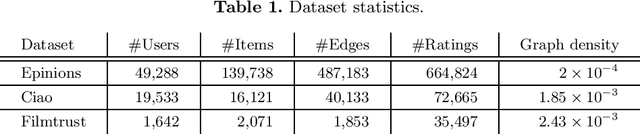
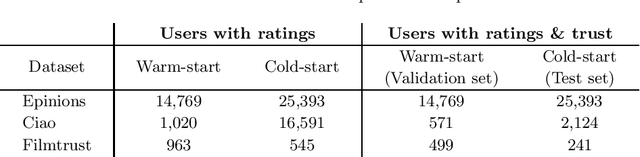
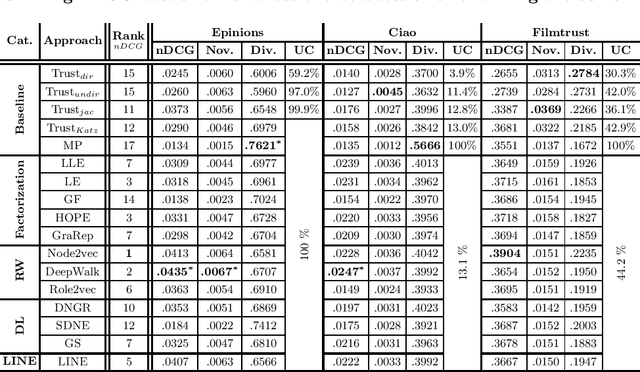
In this work, we study the utility of graph embeddings to generate latent user representations for trust-based collaborative filtering. In a cold-start setting, on three publicly available datasets, we evaluate approaches from four method families: (i) factorization-based, (ii) random walk-based, (iii) deep learning-based, and (iv) the Large-scale Information Network Embedding (LINE) approach. We find that across the four families, random-walk-based approaches consistently achieve the best accuracy. Besides, they result in highly novel and diverse recommendations. Furthermore, our results show that the use of graph embeddings in trust-based collaborative filtering significantly improves user coverage.
* 10 pages, Accepted as a full paper on the 25th International
Symposium on Methodologies for Intelligent Systems (ISMIS'20)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge