Distilling Adversarial Robustness Using Heterogeneous Teachers
Paper and Code
Feb 23, 2024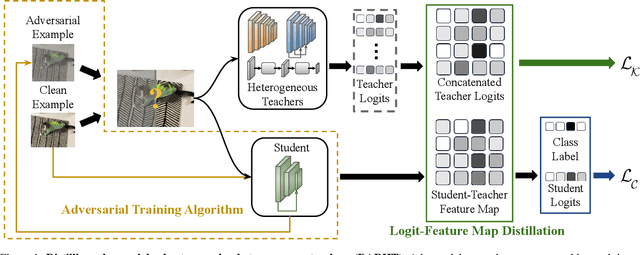
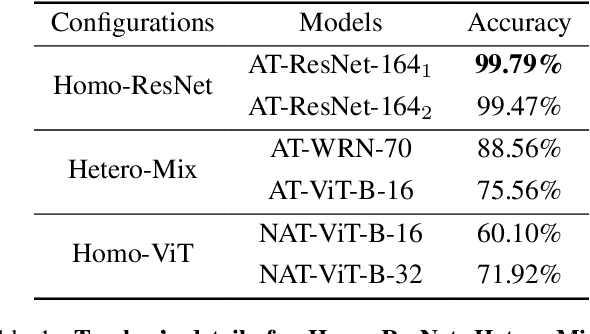
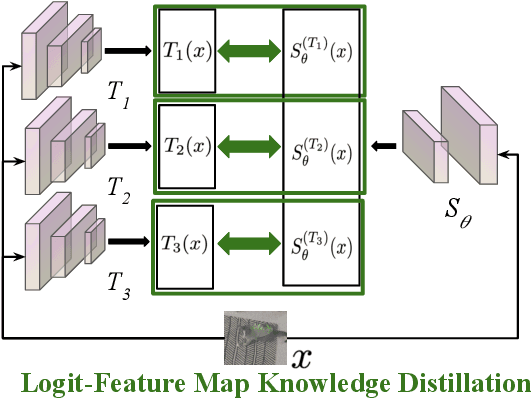
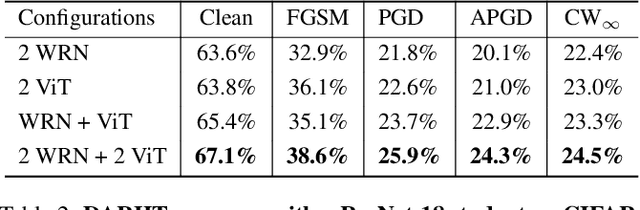
Achieving resiliency against adversarial attacks is necessary prior to deploying neural network classifiers in domains where misclassification incurs substantial costs, e.g., self-driving cars or medical imaging. Recent work has demonstrated that robustness can be transferred from an adversarially trained teacher to a student model using knowledge distillation. However, current methods perform distillation using a single adversarial and vanilla teacher and consider homogeneous architectures (i.e., residual networks) that are susceptible to misclassify examples from similar adversarial subspaces. In this work, we develop a defense framework against adversarial attacks by distilling adversarial robustness using heterogeneous teachers (DARHT). In DARHT, the student model explicitly represents teacher logits in a student-teacher feature map and leverages multiple teachers that exhibit low adversarial example transferability (i.e., exhibit high performance on dissimilar adversarial examples). Experiments on classification tasks in both white-box and black-box scenarios demonstrate that DARHT achieves state-of-the-art clean and robust accuracies when compared to competing adversarial training and distillation methods in the CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and Tiny ImageNet datasets. Comparisons with homogeneous and heterogeneous teacher sets suggest that leveraging teachers with low adversarial example transferability increases student model robustness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge