Deep Learning compatible Differentiable X-ray Projections for Inverse Rendering
Paper and Code
Feb 04, 2021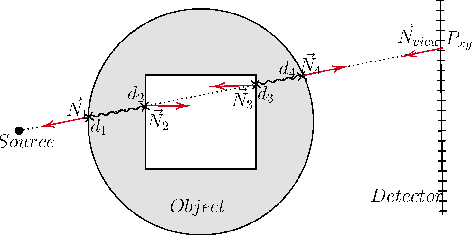
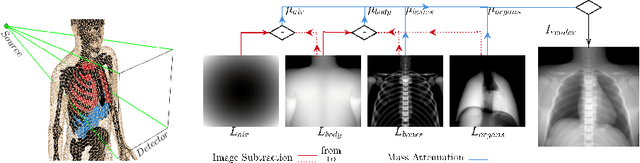

Many minimally invasive interventional procedures still rely on 2D fluoroscopic imaging. Generating a patient-specific 3D model from these X-ray projection data would allow to improve the procedural workflow, e.g. by providing assistance functions such as automatic positioning. To accomplish this, two things are required. First, a statistical human shape model of the human anatomy and second, a differentiable X-ray renderer. In this work, we propose a differentiable renderer by deriving the distance travelled by a ray inside mesh structures to generate a distance map. To demonstrate its functioning, we use it for simulating X-ray images from human shape models. Then we show its application by solving the inverse problem, namely reconstructing 3D models from real 2D fluoroscopy images of the pelvis, which is an ideal anatomical structure for patient registration. This is accomplished by an iterative optimization strategy using gradient descent. With the majority of the pelvis being in the fluoroscopic field of view, we achieve a mean Hausdorff distance of 30 mm between the reconstructed model and the ground truth segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge