Class-incremental learning: survey and performance evaluation
Paper and Code
Oct 28, 2020
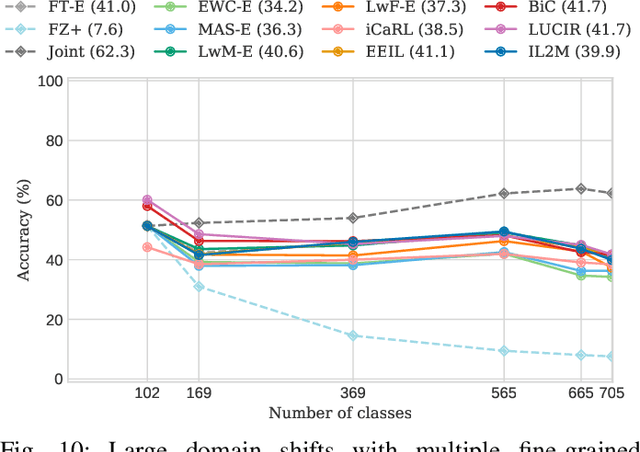
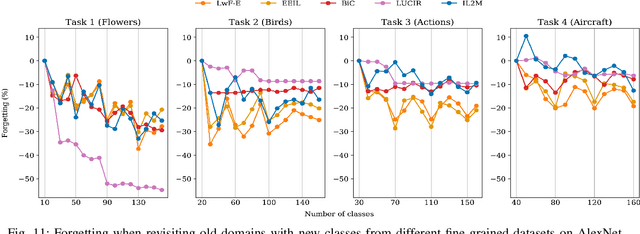
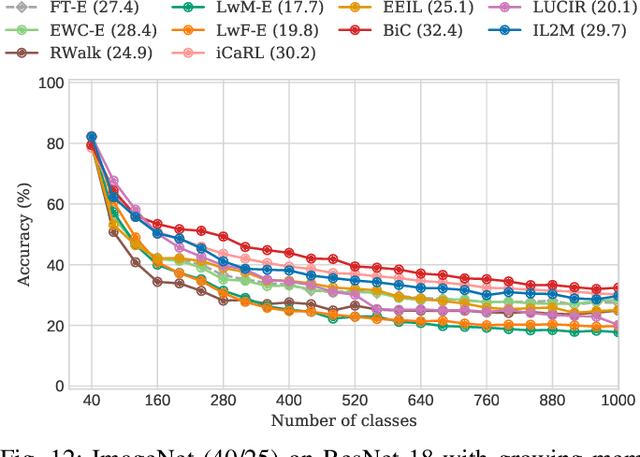
For future learning systems incremental learning is desirable, because it allows for: efficient resource usage by eliminating the need to retrain from scratch at the arrival of new data; reduced memory usage by preventing or limiting the amount of data required to be stored -- also important when privacy limitations are imposed; and learning that more closely resembles human learning. The main challenge for incremental learning is catastrophic forgetting, which refers to the precipitous drop in performance on previously learned tasks after learning a new one. Incremental learning of deep neural networks has seen explosive growth in recent years. Initial work focused on task incremental learning, where a task-ID is provided at inference time. Recently we have seen a shift towards class-incremental learning where the learner must classify at inference time between all classes seen in previous tasks without recourse to a task-ID. In this paper, we provide a complete survey of existing methods for incremental learning, and in particular we perform an extensive experimental evaluation on twelve class-incremental methods. We consider several new experimental scenarios, including a comparison of class-incremental methods on multiple large-scale datasets, investigation into small and large domain shifts, and comparison on various network architectures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge