CatchBackdoor: Backdoor Testing by Critical Trojan Neural Path Identification via Differential Fuzzing
Paper and Code
Dec 24, 2021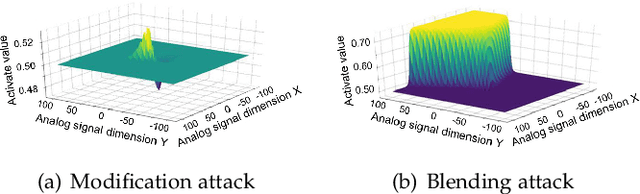
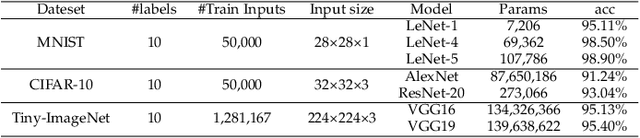
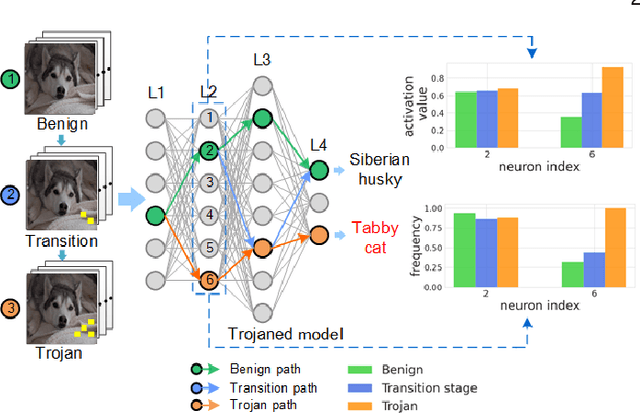
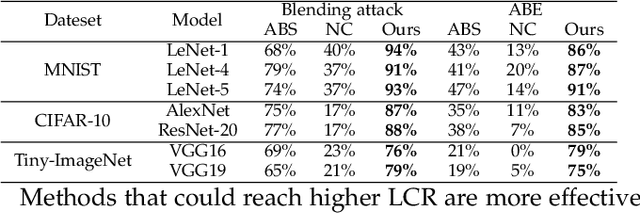
The success of deep neural networks (DNNs) in real-world applications has benefited from abundant pre-trained models. However, the backdoored pre-trained models can pose a significant trojan threat to the deployment of downstream DNNs. Existing DNN testing methods are mainly designed to find incorrect corner case behaviors in adversarial settings but fail to discover the backdoors crafted by strong trojan attacks. Observing the trojan network behaviors shows that they are not just reflected by a single compromised neuron as proposed by previous work but attributed to the critical neural paths in the activation intensity and frequency of multiple neurons. This work formulates the DNN backdoor testing and proposes the CatchBackdoor framework. Via differential fuzzing of critical neurons from a small number of benign examples, we identify the trojan paths and particularly the critical ones, and generate backdoor testing examples by simulating the critical neurons in the identified paths. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of CatchBackdoor, with higher detection performance than existing methods. CatchBackdoor works better on detecting backdoors by stealthy blending and adaptive attacks, which existing methods fail to detect. Moreover, our experiments show that CatchBackdoor may reveal the potential backdoors of models in Model Zoo.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge