Boost AI Power: Data Augmentation Strategies with unlabelled Data and Conformal Prediction, a Case in Alternative Herbal Medicine Discrimination with Electronic Nose
Paper and Code
Feb 05, 2021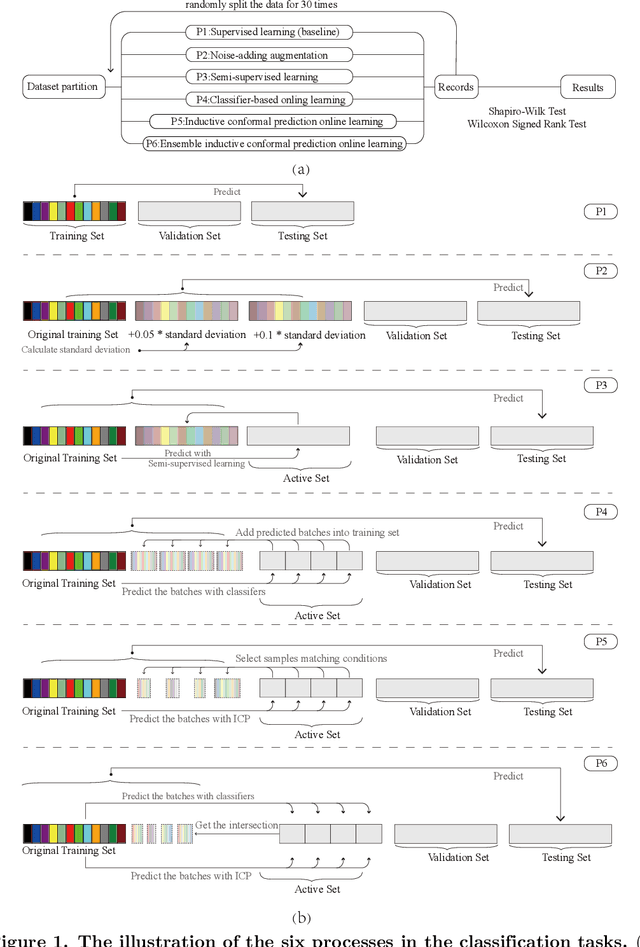
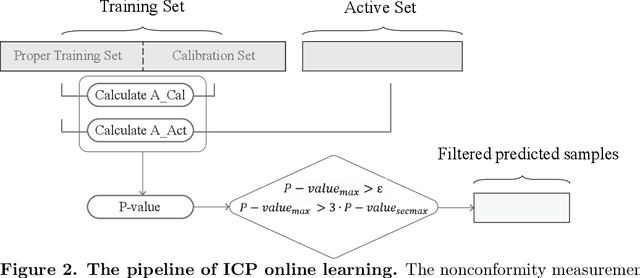
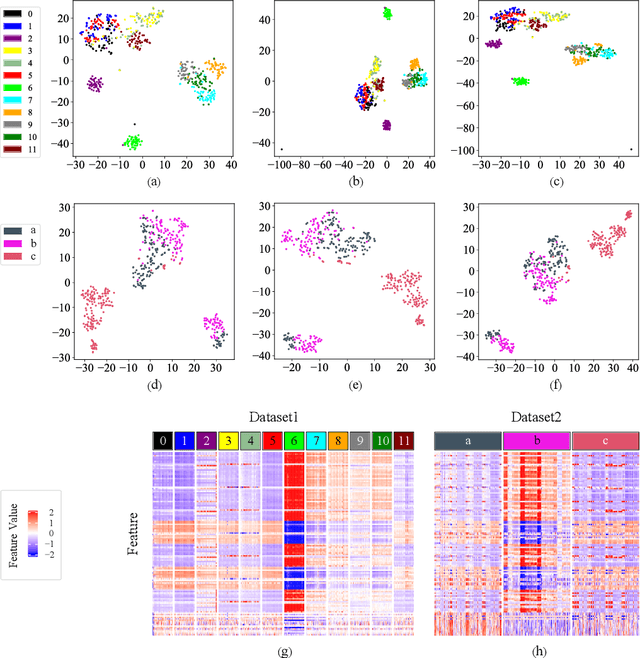
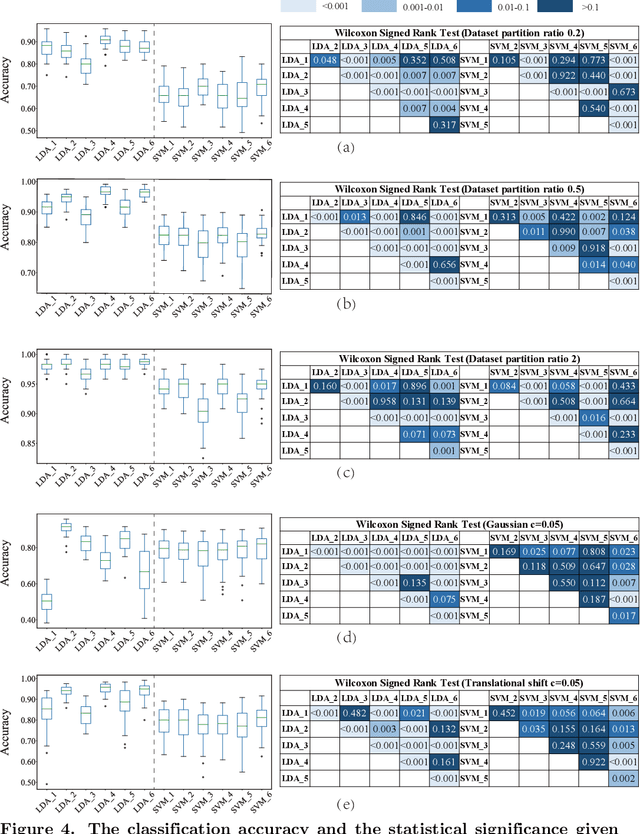
Electronic nose proves its effectiveness in alternativeherbal medicine classification, but due to the supervised learn-ing nature, previous research relies on the labelled training data,which are time-costly and labor-intensive to collect. Consideringthe training data inadequacy in real-world applications, this studyaims to improve classification accuracy via data augmentationstrategies. We stimulated two scenarios to investigate the effective-ness of five data augmentation strategies under different trainingdata inadequacy: in the noise-free scenario, different availability ofunlabelled data were simulated, and in the noisy scenario, differentlevels of Gaussian noises and translational shifts were added tosimulate sensor drifts. The augmentation strategies: noise-addingdata augmentation, semi-supervised learning, classifier-based online learning, inductive conformal prediction (ICP) onlinelearning and the novel ensemble ICP online learning proposed in this study, were compared against supervised learningbaseline, with Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) and Support Vector Machine (SVM) as the classifiers. We found thatat least one strategies significantly improved the classification accuracy with LDA(p<=0.05) and showed non-decreasingclassification accuracy with SVM in each tasks. Moreover, our novel strategy: ensemble ICP online learning outperformedthe others by showing non-decreasing classification accuracy on all tasks and significant improvement on most tasks(25/36 tasks,p<=0.05). This study provides a systematic analysis over augmentation strategies, and we provided userswith recommended strategies under specific circumstances. Furthermore, our newly proposed strategy showed botheffectiveness and robustness in boosting the classification model generalizability, which can also be further employed inother machine learning applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge