Benchmarking Representation Learning for Natural World Image Collections
Paper and Code
Mar 30, 2021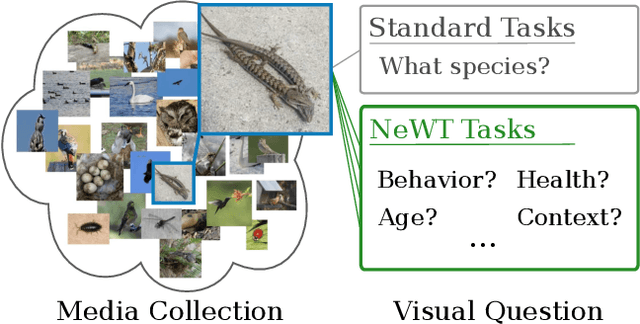
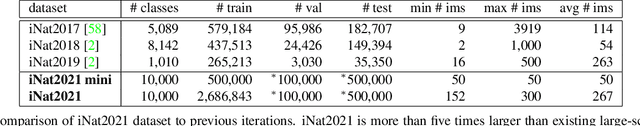
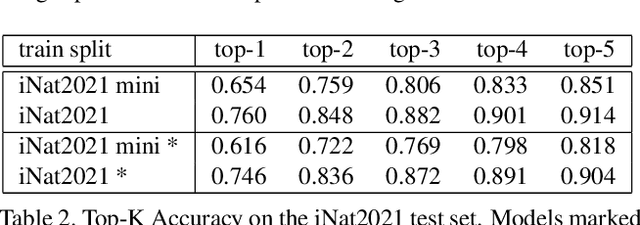

Recent progress in self-supervised learning has resulted in models that are capable of extracting rich representations from image collections without requiring any explicit label supervision. However, to date the vast majority of these approaches have restricted themselves to training on standard benchmark datasets such as ImageNet. We argue that fine-grained visual categorization problems, such as plant and animal species classification, provide an informative testbed for self-supervised learning. In order to facilitate progress in this area we present two new natural world visual classification datasets, iNat2021 and NeWT. The former consists of 2.7M images from 10k different species uploaded by users of the citizen science application iNaturalist. We designed the latter, NeWT, in collaboration with domain experts with the aim of benchmarking the performance of representation learning algorithms on a suite of challenging natural world binary classification tasks that go beyond standard species classification. These two new datasets allow us to explore questions related to large-scale representation and transfer learning in the context of fine-grained categories. We provide a comprehensive analysis of feature extractors trained with and without supervision on ImageNet and iNat2021, shedding light on the strengths and weaknesses of different learned features across a diverse set of tasks. We find that features produced by standard supervised methods still outperform those produced by self-supervised approaches such as SimCLR. However, improved self-supervised learning methods are constantly being released and the iNat2021 and NeWT datasets are a valuable resource for tracking their progress.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge