Attention-based sequence-to-sequence model for speech recognition: development of state-of-the-art system on LibriSpeech and its application to non-native English
Paper and Code
Nov 05, 2018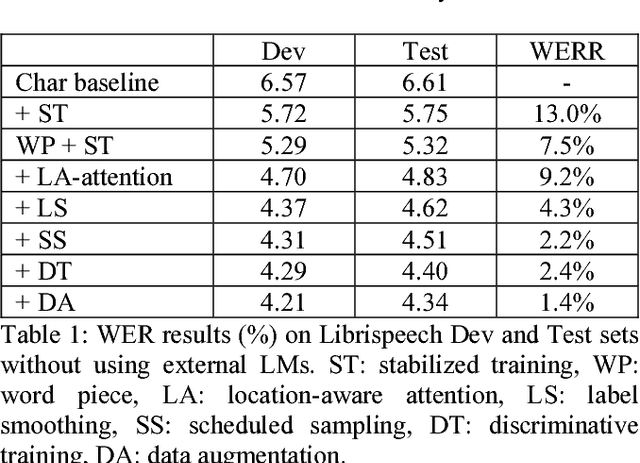
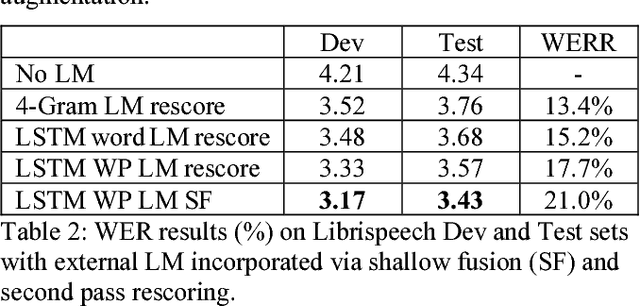
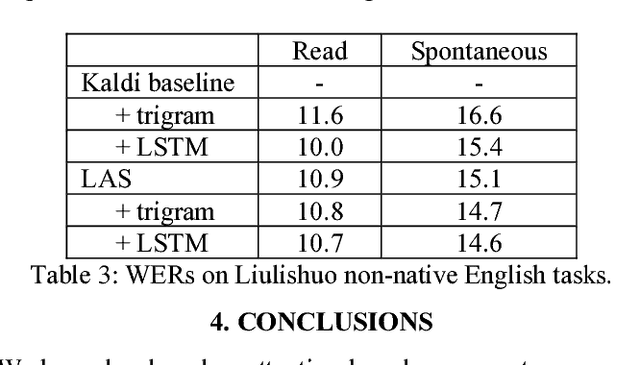
Recent research has shown that attention-based sequence-to-sequence models such as Listen, Attend, and Spell (LAS) yield comparable results to state-of-the-art ASR systems on various tasks. In this paper, we describe the development of such a system and demonstrate its performance on two tasks: first we achieve a new state-of-the-art word error rate of 3.43% on the test clean subset of LibriSpeech English data; second on non-native English speech, including both read speech and spontaneous speech, we obtain very competitive results compared to a conventional system built with the most updated Kaldi recipe.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge