Analysis of Plan-based Retrieval for Grounded Text Generation
Paper and Code
Aug 20, 2024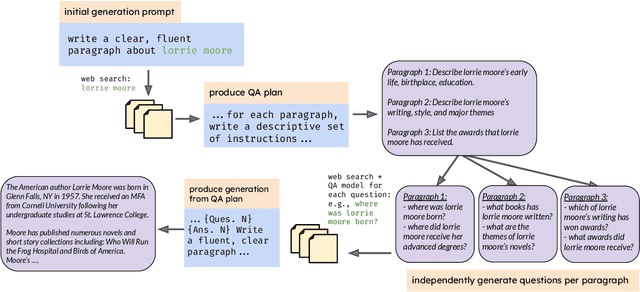
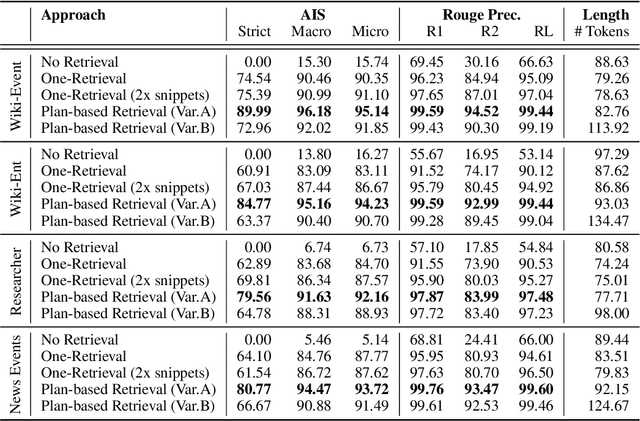
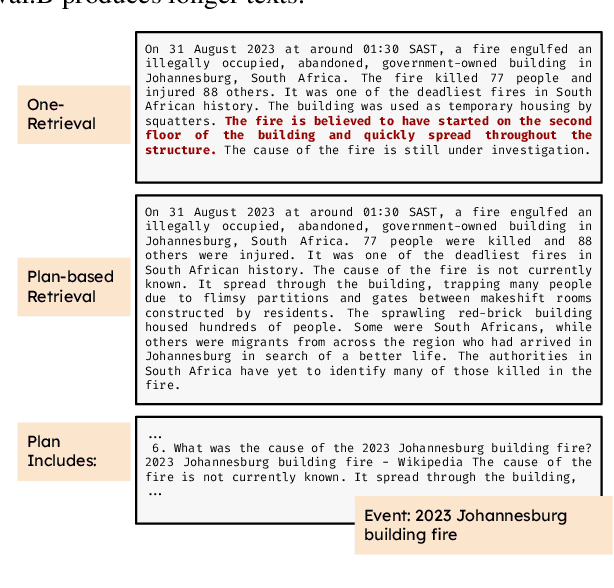
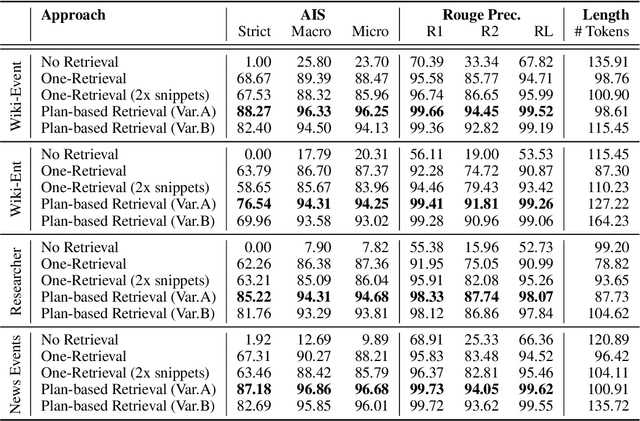
In text generation, hallucinations refer to the generation of seemingly coherent text that contradicts established knowledge. One compelling hypothesis is that hallucinations occur when a language model is given a generation task outside its parametric knowledge (due to rarity, recency, domain, etc.). A common strategy to address this limitation is to infuse the language models with retrieval mechanisms, providing the model with relevant knowledge for the task. In this paper, we leverage the planning capabilities of instruction-tuned LLMs and analyze how planning can be used to guide retrieval to further reduce the frequency of hallucinations. We empirically evaluate several variations of our proposed approach on long-form text generation tasks. By improving the coverage of relevant facts, plan-guided retrieval and generation can produce more informative responses while providing a higher rate of attribution to source documents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge