An Upper Confidence Bound for Simultaneous Exploration and Exploitation in Heterogeneous Multi-Robot Systems
Paper and Code
May 13, 2021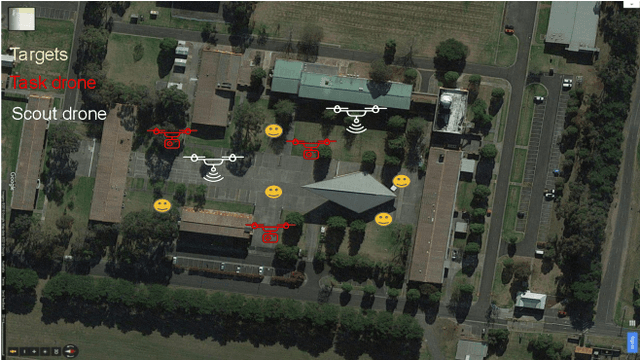
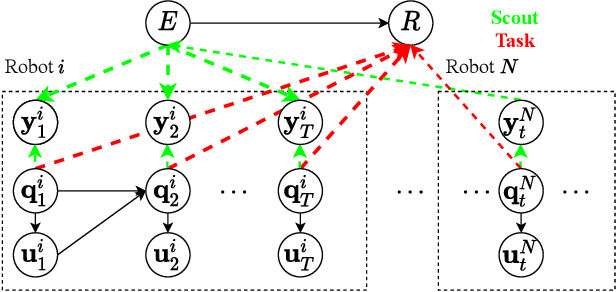
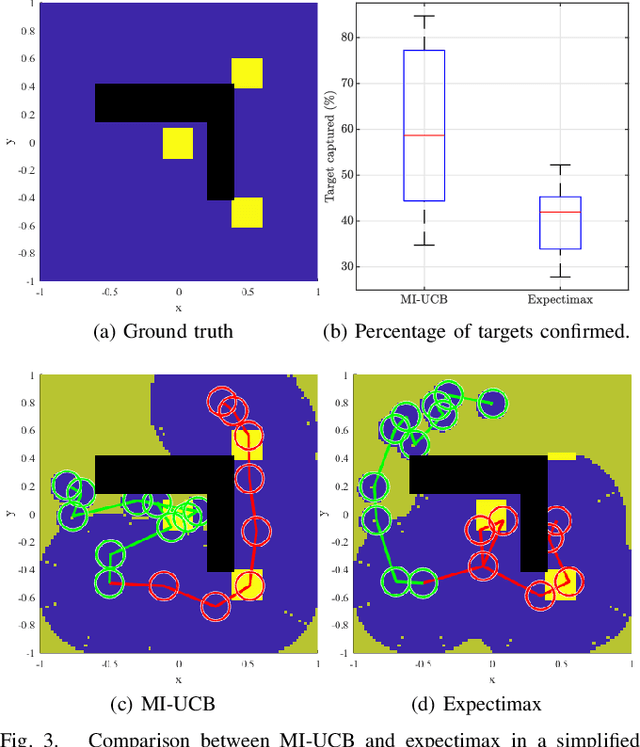
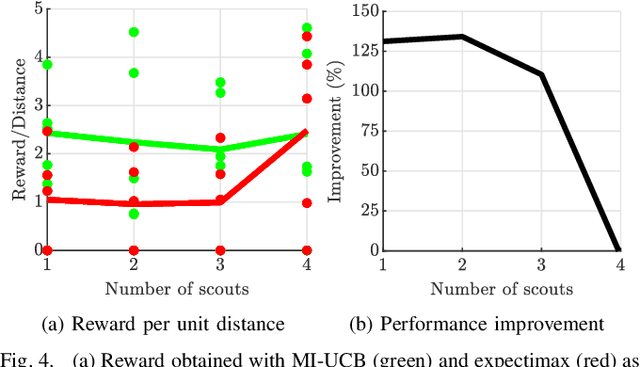
Heterogeneous multi-robot systems are advantageous for operations in unknown environments because functionally specialised robots can gather environmental information, while others perform tasks. We define this decomposition as the scout-task robot architecture and show how it avoids the need to explicitly balance exploration and exploitation~by permitting the system to do both simultaneously. The challenge is to guide exploration in a way that improves overall performance for time-limited tasks. We derive a novel upper confidence bound for simultaneous exploration and exploitation based on mutual information and present a general solution for scout-task coordination using decentralised Monte Carlo tree search. We evaluate the performance of our algorithms in a multi-drone surveillance scenario in which scout robots are equipped with low-resolution, long-range sensors and task robots capture detailed information using short-range sensors. The results address a new class of coordination problem for heterogeneous teams that has many practical applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge