Achieving Dexterous Bidirectional Interaction in Uncertain Conditions for Medical Robotics
Paper and Code
Jun 20, 2022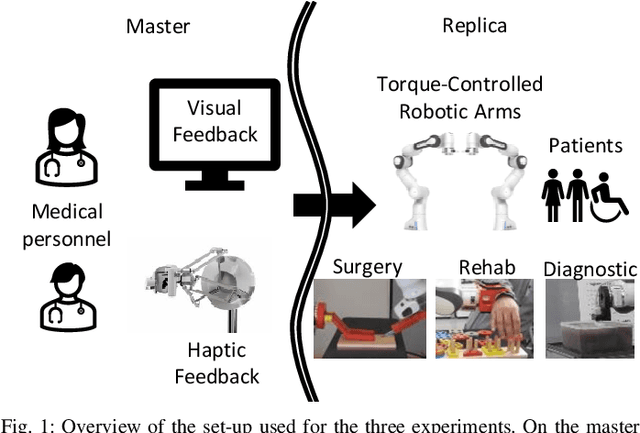
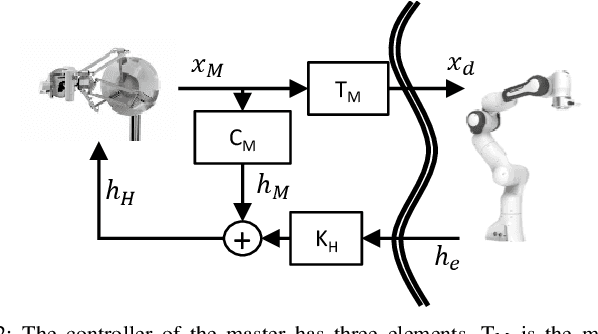
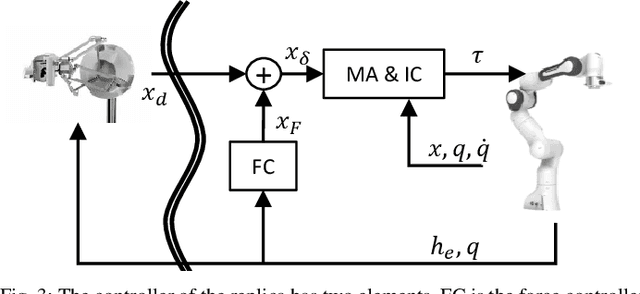
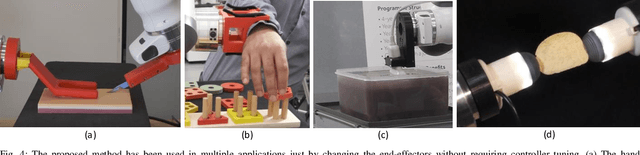
Medical robotics can help improve and extend the reach of healthcare services. A major challenge for medical robots is the complex physical interaction between the robot and the patients which is required to be safe. This work presents the preliminary evaluation of a recently introduced control architecture based on the Fractal Impedance Control (FIC) in medical applications. The deployed FIC architecture is robust to delay between the master and the replica robots. It can switch online between an admittance and impedance behaviour, and it is robust to interaction with unstructured environments. Our experiments analyse three scenarios: teleoperated surgery, rehabilitation, and remote ultrasound scan. The experiments did not require any adjustment of the robot tuning, which is essential in medical applications where the operators do not have an engineering background required to tune the controller. Our results show that is possible to teleoperate the robot to cut using a scalpel, do an ultrasound scan, and perform remote occupational therapy. However, our experiments also highlighted the need for a better robots embodiment to precisely control the system in 3D dynamic tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge