A Privacy-Preserving Unsupervised Domain Adaptation Framework for Clinical Text Analysis
Paper and Code
Jan 18, 2022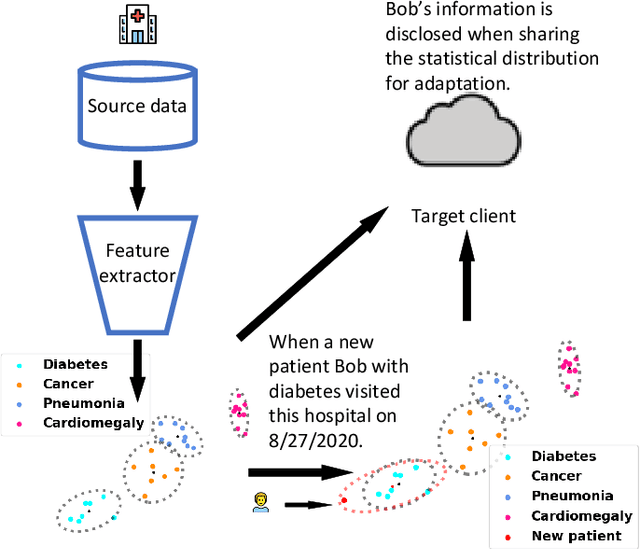
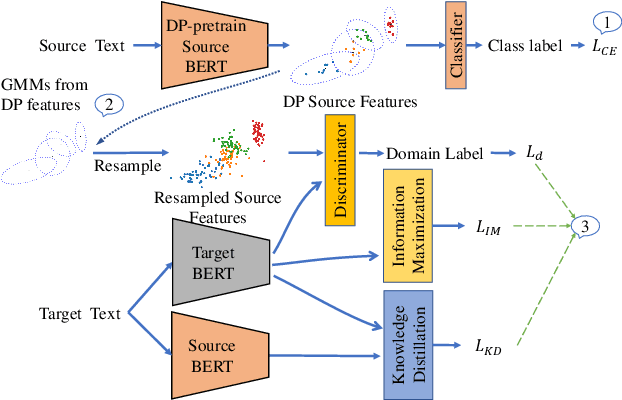
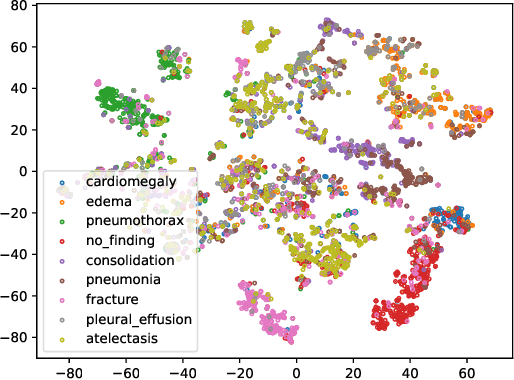
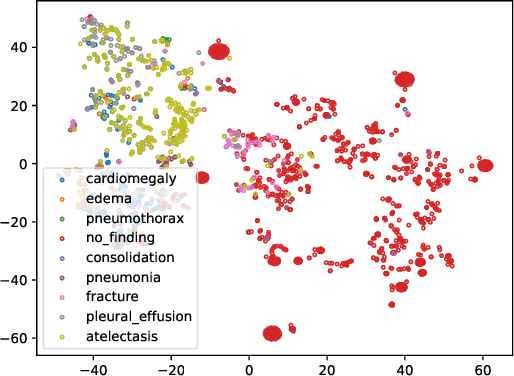
Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) generally aligns the unlabeled target domain data to the distribution of the source domain to mitigate the distribution shift problem. The standard UDA requires sharing the source data with the target, having potential data privacy leaking risks. To protect the source data's privacy, we first propose to share the source feature distribution instead of the source data. However, sharing only the source feature distribution may still suffer from the membership inference attack who can infer an individual's membership by the black-box access to the source model. To resolve this privacy issue, we further study the under-explored problem of privacy-preserving domain adaptation and propose a method with a novel differential privacy training strategy to protect the source data privacy. We model the source feature distribution by Gaussian Mixture Models (GMMs) under the differential privacy setting and send it to the target client for adaptation. The target client resamples differentially private source features from GMMs and adapts on target data with several state-of-art UDA backbones. With our proposed method, the source data provider could avoid leaking source data privacy during domain adaptation as well as reserve the utility. To evaluate our proposed method's utility and privacy loss, we apply our model on a medical report disease label classification task using two noisy challenging clinical text datasets. The results show that our proposed method can preserve source data's privacy with a minor performance influence on the text classification task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge