A multi-cohort study on prediction of acute brain dysfunction states using selective state space models
Paper and Code
Mar 11, 2024

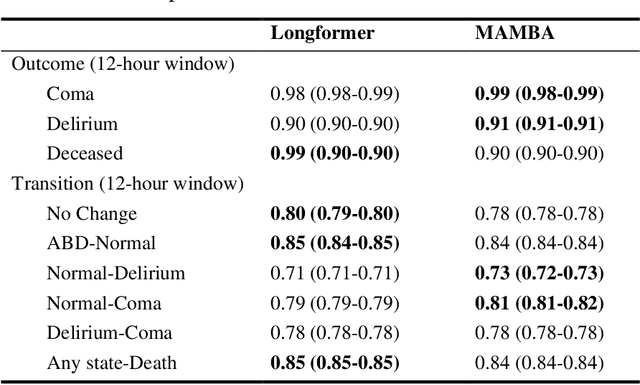

Assessing acute brain dysfunction (ABD), including delirium and coma in the intensive care unit (ICU), is a critical challenge due to its prevalence and severe implications for patient outcomes. Current diagnostic methods rely on infrequent clinical observations, which can only determine a patient's ABD status after onset. Our research attempts to solve these problems by harnessing Electronic Health Records (EHR) data to develop automated methods for ABD prediction for patients in the ICU. Existing models solely predict a single state (e.g., either delirium or coma), require at least 24 hours of observation data to make predictions, do not dynamically predict fluctuating ABD conditions during ICU stay (typically a one-time prediction), and use small sample size, proprietary single-hospital datasets. Our research fills these gaps in the existing literature by dynamically predicting delirium, coma, and mortality for 12-hour intervals throughout an ICU stay and validating on two public datasets. Our research also introduces the concept of dynamically predicting critical transitions from non-ABD to ABD and between different ABD states in real time, which could be clinically more informative for the hospital staff. We compared the predictive performance of two state-of-the-art neural network models, the MAMBA selective state space model and the Longformer Transformer model. Using the MAMBA model, we achieved a mean area under the receiving operator characteristic curve (AUROC) of 0.95 on outcome prediction of ABD for 12-hour intervals. The model achieves a mean AUROC of 0.79 when predicting transitions between ABD states. Our study uses a curated dataset from the University of Florida Health Shands Hospital for internal validation and two publicly available datasets, MIMIC-IV and eICU, for external validation, demonstrating robustness across ICU stays from 203 hospitals and 140,945 patients.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge