A Comparison of Label-Synchronous and Frame-Synchronous End-to-End Models for Speech Recognition
Paper and Code
May 25, 2020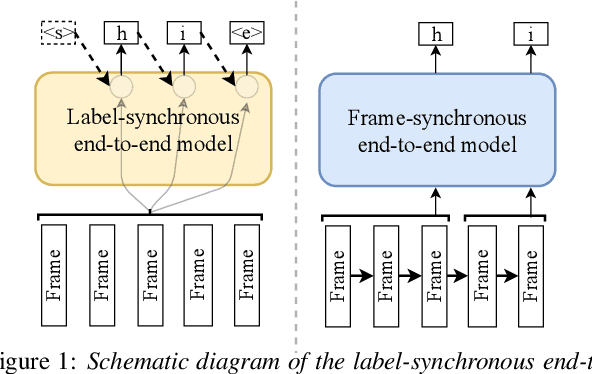
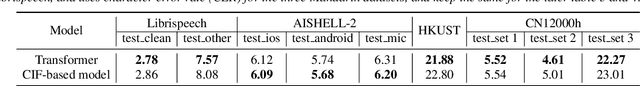
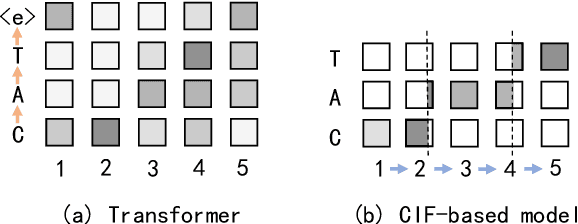
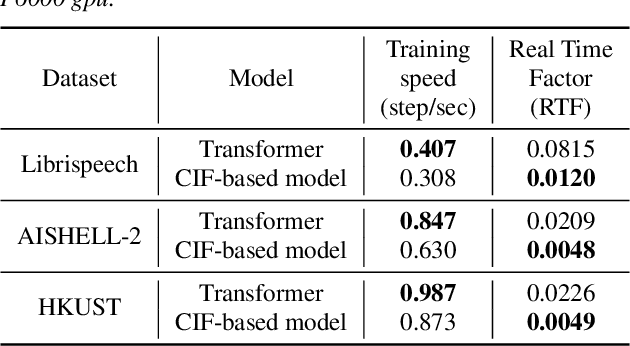
End-to-end models are gaining wider attention in the field of automatic speech recognition (ASR). One of their advantages is the simplicity of building that directly recognizes the speech frame sequence into the text label sequence by neural networks. According to the driving end in the recognition process, end-to-end ASR models could be categorized into two types: label-synchronous and frame-synchronous, each of which has unique model behaviour and characteristic. In this work, we make a detailed comparison on a representative label-synchronous model (transformer) and a soft frame-synchronous model (continuous integrate-and-fire (CIF) based model). The results on three public dataset and a large-scale dataset with 12000 hours of training data show that the two types of models have respective advantages that are consistent with their synchronous mode.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge