A Compact DNN: Approaching GoogLeNet-Level Accuracy of Classification and Domain Adaptation
Paper and Code
Apr 03, 2017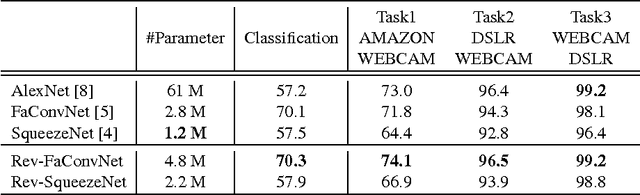
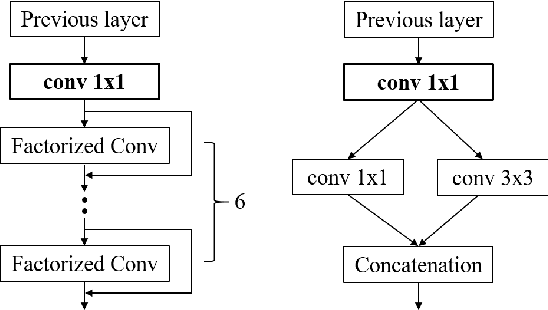
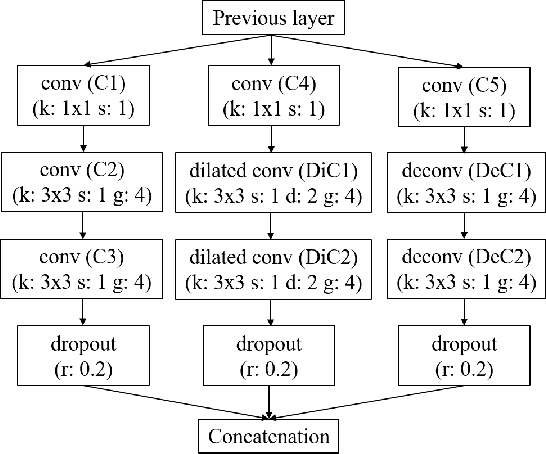
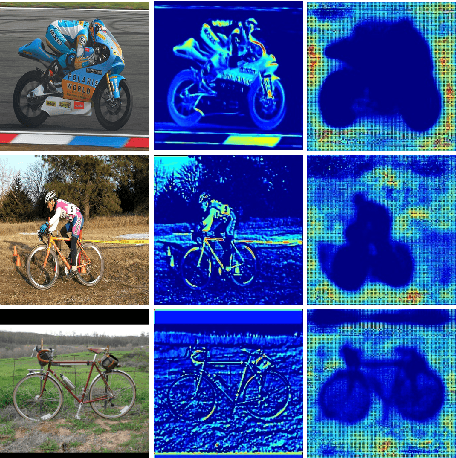
Recently, DNN model compression based on network architecture design, e.g., SqueezeNet, attracted a lot attention. No accuracy drop on image classification is observed on these extremely compact networks, compared to well-known models. An emerging question, however, is whether these model compression techniques hurt DNN's learning ability other than classifying images on a single dataset. Our preliminary experiment shows that these compression methods could degrade domain adaptation (DA) ability, though the classification performance is preserved. Therefore, we propose a new compact network architecture and unsupervised DA method in this paper. The DNN is built on a new basic module Conv-M which provides more diverse feature extractors without significantly increasing parameters. The unified framework of our DA method will simultaneously learn invariance across domains, reduce divergence of feature representations, and adapt label prediction. Our DNN has 4.1M parameters, which is only 6.7% of AlexNet or 59% of GoogLeNet. Experiments show that our DNN obtains GoogLeNet-level accuracy both on classification and DA, and our DA method slightly outperforms previous competitive ones. Put all together, our DA strategy based on our DNN achieves state-of-the-art on sixteen of total eighteen DA tasks on popular Office-31 and Office-Caltech datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge