Ziwei Shi
L2RSI: Cross-view LiDAR-based Place Recognition for Large-scale Urban Scenes via Remote Sensing Imagery
Mar 14, 2025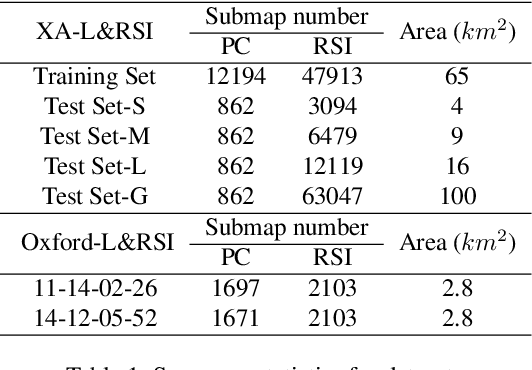
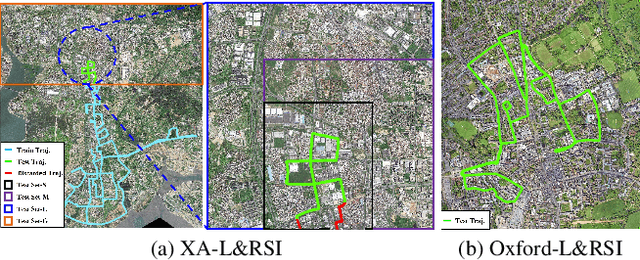
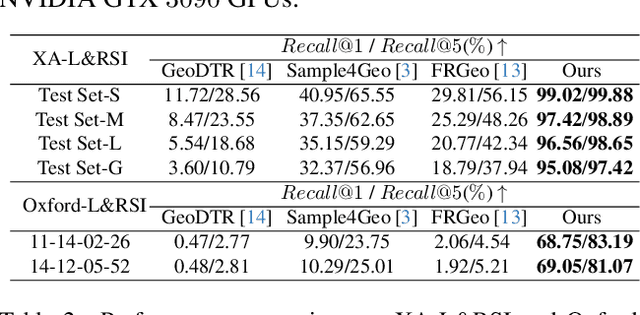
Abstract:We tackle the challenge of LiDAR-based place recognition, which traditionally depends on costly and time-consuming prior 3D maps. To overcome this, we first construct XA-L&RSI dataset, which encompasses approximately $110,000$ remote sensing submaps and $13,000$ LiDAR point cloud submaps captured in urban scenes, and propose a novel method, L2RSI, for cross-view LiDAR place recognition using high-resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. This approach enables large-scale localization capabilities at a reduced cost by leveraging readily available overhead images as map proxies. L2RSI addresses the dual challenges of cross-view and cross-modal place recognition by learning feature alignment between point cloud submaps and remote sensing submaps in the semantic domain. Additionally, we introduce a novel probability propagation method based on a dynamic Gaussian mixture model to refine position predictions, effectively leveraging temporal and spatial information. This approach enables large-scale retrieval and cross-scene generalization without fine-tuning. Extensive experiments on XA-L&RSI demonstrate that, within a $100km^2$ retrieval range, L2RSI accurately localizes $95.08\%$ of point cloud submaps within a $30m$ radius for top-$1$ retrieved location. We provide a video to more vividly display the place recognition results of L2RSI at https://shizw695.github.io/L2RSI/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge