Ziliang Zhang
Can LLMs Generate Reliable Test Case Generators? A Study on Competition-Level Programming Problems
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in code generation, capable of tackling complex tasks during inference. However, the extent to which LLMs can be utilized for code checking or debugging through test case generation remains largely unexplored. We investigate this problem from the perspective of competition-level programming (CP) programs and propose TCGBench, a Benchmark for (LLM generation of) Test Case Generators. This benchmark comprises two tasks, aimed at studying the capabilities of LLMs in (1) generating valid test case generators for a given CP problem, and further (2) generating targeted test case generators that expose bugs in human-written code. Experimental results indicate that while state-of-the-art LLMs can generate valid test case generators in most cases, most LLMs struggle to generate targeted test cases that reveal flaws in human code effectively. Especially, even advanced reasoning models (e.g., o3-mini) fall significantly short of human performance in the task of generating targeted generators. Furthermore, we construct a high-quality, manually curated dataset of instructions for generating targeted generators. Analysis demonstrates that the performance of LLMs can be enhanced with the aid of this dataset, by both prompting and fine-tuning.
BOXR: Body and head motion Optimization framework for eXtended Reality
Oct 16, 2024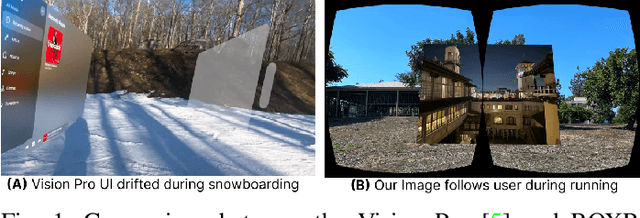
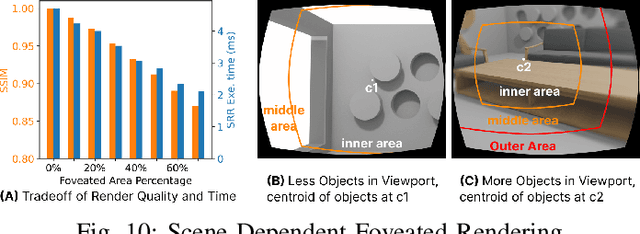
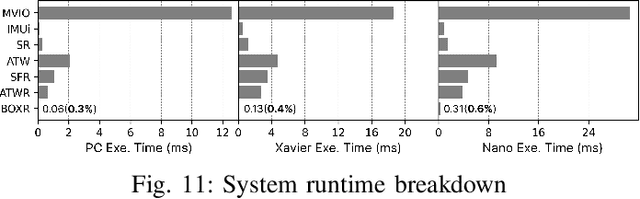
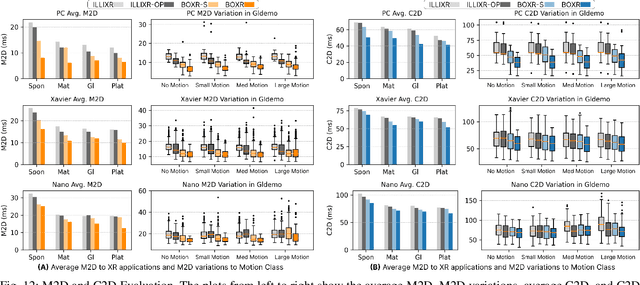
Abstract:The emergence of standalone XR systems has enhanced user mobility, accommodating both subtle, frequent head motions and substantial, less frequent body motions. However, the pervasively used M2D latency metric, which measures the delay between the most recent motion and its corresponding display update, only accounts for head motions. This oversight can leave users prone to motion sickness if significant body motion is involved. Although existing methods optimize M2D latency through asynchronous task scheduling and reprojection methods, they introduce challenges like resource contention between tasks and outdated pose data. These challenges are further complicated by user motion dynamics and scene changes during runtime. To address these issues, we for the first time introduce the C2D latency metric, which captures the delay caused by body motions, and present BOXR, a framework designed to co-optimize both body and head motion delays within an XR system. BOXR enhances the coordination between M2D and C2D latencies by efficiently scheduling tasks to avoid contentions while maintaining an up-to-date pose in the output frame. Moreover, BOXR incorporates a motion-driven visual inertial odometer to adjust to user motion dynamics and employs scene-dependent foveated rendering to manage changes in the scene effectively. Our evaluations show that BOXR significantly outperforms state-of-the-art solutions in 11 EuRoC MAV datasets across 4 XR applications across 3 hardware platforms. In controlled motion and scene settings, BOXR reduces M2D and C2D latencies by up to 63% and 27%, respectively and increases frame rate by up to 43%. In practical deployments, BOXR achieves substantial reductions in real-world scenarios up to 42% in M2D latency and 31% in C2D latency while maintaining remarkably low miss rates of only 1.6% for M2D requirements and 1.0% for C2D requirements.
OceanCastNet: A Deep Learning Ocean Wave Model with Energy Conservation
Jun 09, 2024Abstract:Traditional wave forecasting models, although based on energy conservation equations, are computationally expensive. On the other hand, existing deep learning geophysical fluid models, while computationally efficient, often suffer from issues such as energy dissipation in long-term forecasts. This paper proposes a novel energy-balanced deep learning wave forecasting model called OceanCastNet (OCN). By incorporating wind fields at the current, previous, and future time steps, as well as wave fields at the current and previous time steps as input variables, OCN maintains energy balance within the model. Furthermore, the model employs adaptive Fourier operators as its core components and designs a masked loss function to better handle the impact of land-sea boundaries. A series of experiments on the ERA5 dataset demonstrate that OCN can achieve short-term forecast accuracy comparable to traditional models while exhibiting an understanding of the wave generation process. In comparative experiments under both normal and extreme conditions, OCN consistently outperforms the widely used WaveWatch III model in the industry. Even after long-term forecasting, OCN maintains a stable and energy-rich state. By further constructing a simple meteorological model, OCN-wind, which considers energy balance, this paper confirms the importance of energy constraints for improving the long-term forecast performance of deep learning meteorological models. This finding provides new ideas for future research on deep learning geophysical fluid models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge