Zijun Frank Zhang
Better Prompt Compression Without Multi-Layer Perceptrons
Jan 12, 2025



Abstract:Prompt compression is a promising approach to speeding up language model inference without altering the generative model. Prior works compress prompts into smaller sequences of learned tokens using an encoder that is trained as a LowRank Adaptation (LoRA) of the inference language model. However, we show that the encoder does not need to keep the original language model's architecture to achieve useful compression. We introduce the Attention-Only Compressor (AOC), which learns a prompt compression encoder after removing the multilayer perceptron (MLP) layers in the Transformer blocks of a language model, resulting in an encoder with roughly 67% less parameters compared to the original model. Intriguingly we find that, across a range of compression ratios up to 480x, AOC can better regenerate prompts and outperform a baseline compression encoder that is a LoRA of the inference language model without removing MLP layers. These results demonstrate that the architecture of prompt compression encoders does not need to be identical to that of the original decoder language model, paving the way for further research into architectures and approaches for prompt compression.
Long-range gene expression prediction with token alignment of large language model
Oct 02, 2024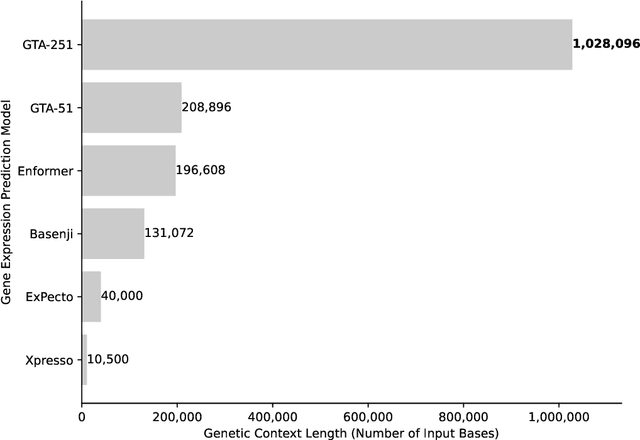
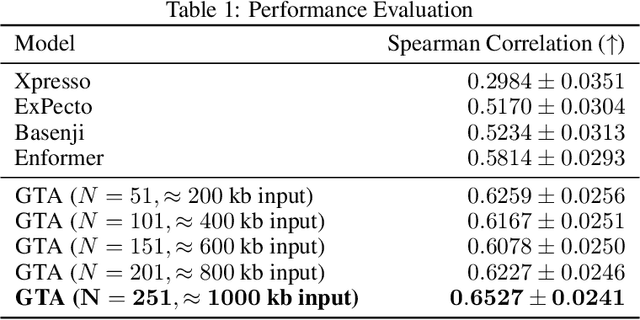
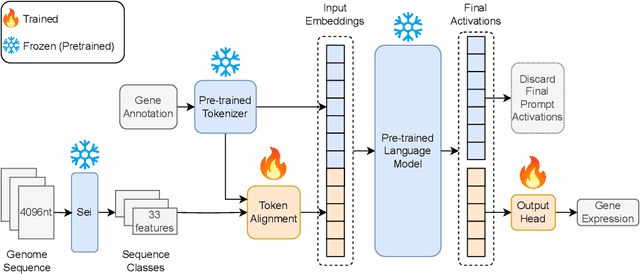
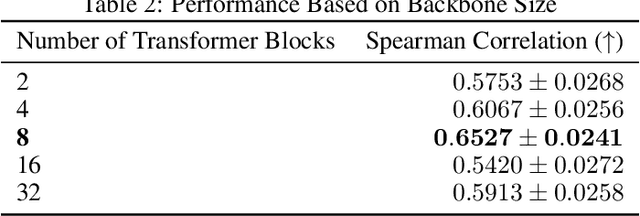
Abstract:Gene expression is a cellular process that plays a fundamental role in human phenotypical variations and diseases. Despite advances of deep learning models for gene expression prediction, recent benchmarks have revealed their inability to learn distal regulatory grammar. Here, we address this challenge by leveraging a pretrained large language model to enhance gene expression prediction. We introduce Genetic sequence Token Alignment (GTA), which aligns genetic sequence features with natural language tokens, allowing for symbolic reasoning of genomic sequence features via the frozen language model. This cross-modal adaptation learns the regulatory grammar and allows us to further incorporate gene-specific human annotations as prompts, enabling in-context learning that is not possible with existing models. Trained on lymphoblastoid cells, GTA was evaluated on cells from the Geuvadis consortium and outperforms state-of-the-art models such as Enformer, achieving a Spearman correlation of 0.65, a 10\% improvement. Additionally, GTA offers improved interpretation of long-range interactions through the identification of the most meaningful sections of the input genetic context. GTA represents a powerful and novel cross-modal approach to gene expression prediction by utilizing a pretrained language model, in a paradigm shift from conventional gene expression models trained only on sequence data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge