Zhongwei Ren
VideoWorld: Exploring Knowledge Learning from Unlabeled Videos
Jan 16, 2025Abstract:This work explores whether a deep generative model can learn complex knowledge solely from visual input, in contrast to the prevalent focus on text-based models like large language models (LLMs). We develop VideoWorld, an auto-regressive video generation model trained on unlabeled video data, and test its knowledge acquisition abilities in video-based Go and robotic control tasks. Our experiments reveal two key findings: (1) video-only training provides sufficient information for learning knowledge, including rules, reasoning and planning capabilities, and (2) the representation of visual change is crucial for knowledge acquisition. To improve both the efficiency and efficacy of this process, we introduce the Latent Dynamics Model (LDM) as a key component of VideoWorld. Remarkably, VideoWorld reaches a 5-dan professional level in the Video-GoBench with just a 300-million-parameter model, without relying on search algorithms or reward mechanisms typical in reinforcement learning. In robotic tasks, VideoWorld effectively learns diverse control operations and generalizes across environments, approaching the performance of oracle models in CALVIN and RLBench. This study opens new avenues for knowledge acquisition from visual data, with all code, data, and models open-sourced for further research.
PixelLM: Pixel Reasoning with Large Multimodal Model
Dec 04, 2023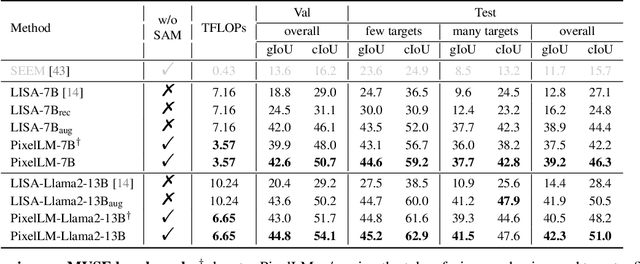
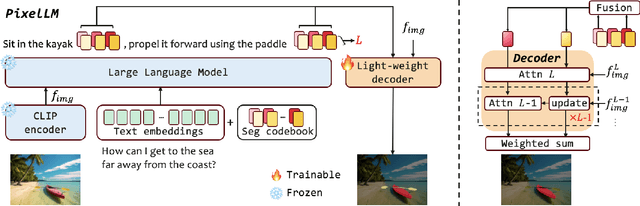
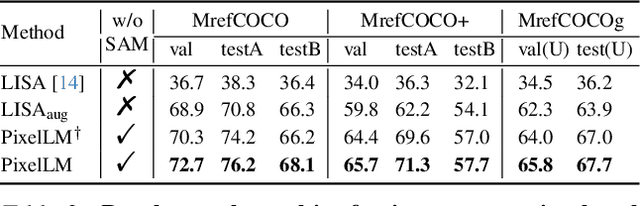
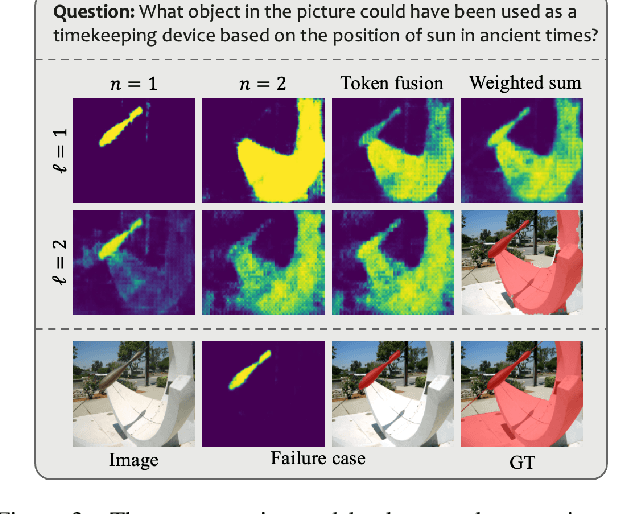
Abstract:While large multimodal models (LMMs) have achieved remarkable progress, generating pixel-level masks for image reasoning tasks involving multiple open-world targets remains a challenge. To bridge this gap, we introduce PixelLM, an effective and efficient LMM for pixel-level reasoning and understanding. Central to PixelLM is a novel, lightweight pixel decoder and a comprehensive segmentation codebook. The decoder efficiently produces masks from the hidden embeddings of the codebook tokens, which encode detailed target-relevant information. With this design, PixelLM harmonizes with the structure of popular LMMs and avoids the need for additional costly segmentation models. Furthermore, we propose a target refinement loss to enhance the model's ability to differentiate between multiple targets, leading to substantially improved mask quality. To advance research in this area, we construct MUSE, a high-quality multi-target reasoning segmentation benchmark. PixelLM excels across various pixel-level image reasoning and understanding tasks, outperforming well-established methods in multiple benchmarks, including MUSE, single- and multi-referring segmentation. Comprehensive ablations confirm the efficacy of each proposed component. All code, models, and datasets will be publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge